Use of Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer for Different Crops
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) fertilizer is one of the most widely used phosphorus-based fertilizers in agriculture, known for its high nutrient content and immediate availability. DAP contains both phosphorus (46% P₂O₅) and nitrogen (18% N), making it effective for early crop growth and overall plant development. This article explores the best practices for the use of diammonium phosphate fertilizer across various crops and how it enhances yield and crop quality.
DAP contains 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus (as P₂O₅), making it highly effective for early crop development. Phosphorus is essential for photosynthesis, root establishment, and energy transfer, while nitrogen contributes to chlorophyll production and leaf growth. The use of diammonium phosphate ensures that crops receive these vital nutrients in a readily available form. Moreover, when DAP dissolves, it temporarily raises the soil pH, improving nutrient availability and encouraging root uptake.
How to Use Diammonium Phosphate for Different Crops

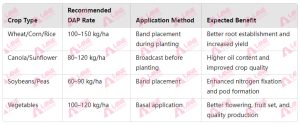
Cereals (Wheat, Corn, Rice)
Cereals require phosphorus for strong root systems and nitrogen for lush foliage development.
- Application Method: Band DAP near the seed during planting to ensure early access to nutrients.
- Recommended Rate: 100–150 kg/ha, depending on soil fertility levels.
- Benefit: The use of diammonium phosphate in cereals supports uniform germination and increases grain yield.
Oilseeds (Canola, Sunflower)
Oilseeds depend on phosphorus for metabolic processes that enhance oil production and nitrogen for healthy plant growth.
- Application Method: Broadcast DAP before planting or incorporate it into the soil.
- Recommended Rate: 80–120 kg/ha.
- Benefit: Proper use of diammonium phosphate ensures higher oil content and stronger plant growth.
Legumes (Soybeans, Peas)
Although legumes can fix nitrogen, they require phosphorus to facilitate root development and pod formation.
- Application Method: Band DAP during planting, avoiding direct contact with seeds.
- Recommended Rate: 60–90 kg/ha.
- Benefit: The use of diammonium phosphate in legumes improves nitrogen fixation and pod quality.
Fruits and Vegetables
Phosphorus is vital for root growth and flowering in fruits and vegetables, while nitrogen helps maintain lush foliage.
- Application Method: Apply DAP as a basal fertilizer during planting.
- Recommended Rate: 100–120 kg/ha, adjusted for crop type.
- Benefit: The use of diammonium phosphate encourages early root establishment and improves fruit setting and quality.
Factors to Consider When Using Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer

DAP fertilizer maker
Soil Type and pH
DAP works well across a range of soils but performs best in slightly acidic to neutral soils. Upon application, DAP dissolves and temporarily raises soil pH, which improves nutrient availability. However, in alkaline soils, DAP may need to be supplemented with sulfur-based fertilizers to balance pH.
Timing and Placement
- Timing: Apply DAP at the start of the crop cycle, either during planting or just before. Early application ensures that plants have access to essential nutrients during the most critical growth stages.
- Placement: For most crops, band placement 5–7 cm from the seed prevents nutrient lock-up and seed damage, maximizing uptake efficiency.
Common Application Rates of DAP Fertilizer
Best Practices for the Use of Diammonium Phosphate
- Integrate with Organic Fertilizers
Combining DAP with organic fertilizers improves soil health and nutrient availability. - Monitor Soil Nutrients Regularly
Soil testing ensures the correct use of diammonium phosphate, preventing over-fertilization and nutrient imbalances. - Irrigate After Application
Watering after DAP application promotes fertilizer dissolution and nutrient uptake. - Use in Crop Rotation Systems
Applying DAP in crop rotation helps maintain soil fertility and improves long-term crop yields.
Benefits of Using Diammonium Phosphate Fertilizer
- Promotes Early Root Growth: DAP provides readily available phosphorus, essential for early-stage root development.
- Boosts Crop Yield: The nitrogen in DAP enhances foliage growth, resulting in higher yields.
- Improves Soil Health: Phosphorus supports microbial activity, improving soil fertility over time.
- Reduces Nutrient Deficiency: Regular use of diammonium phosphate ensures crops receive sufficient phosphorus and nitrogen to thrive.
Conclusion
The use of diammonium phosphate fertilizer is essential for modern agriculture, providing a balanced supply of phosphorus and nitrogen to support crop growth and productivity. Whether applied to cereals, legumes, or vegetables, DAP promotes early root development, improves nutrient uptake, and enhances yields.
By following best practices—such as proper placement, timing, and soil testing—farmers can maximize the benefits of DAP and ensure sustainable agricultural practices. With effective use of diammonium phosphate, crops grow healthier, yields increase, and soil fertility is maintained, supporting long-term agricultural success.





Send a message to us