Triple Superphosphate and DAP: Which Fertilizer is Best for Your Crops?
When it comes to enhancing soil fertility and promoting robust crop growth, selecting the right type of fertilizer is crucial. Among the various types of fertilizers available, Triple Superphosphate and DAP are two of the most widely used phosphorus-based fertilizers. Both fertilizers provide essential nutrients to plants, but their composition, nutrient balance, and ideal application vary.In this article, we will compare Triple Superphosphate and DAP to help you determine which fertilizer is best suited for your crops.
What is Triple Superphosphate (TSP)?

Triple Superphosphate (TSP) is a highly concentrated fertilizer that contains around 46% phosphorus (as P2O5, or phosphorus pentoxide). It is produced by treating phosphate rock with concentrated phosphoric acid, resulting in a fertilizer that is rich in water-soluble phosphorus, which is readily available to plants. TSP is often used for crops that require an immediate boost of phosphorus and is particularly effective in acidic soils where phosphorus is typically less available.
What is Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)?

Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer containing 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus (as P2O5). DAP is produced by reacting ammonia with phosphoric acid, resulting in a compound that provides both nitrogen and phosphorus to plants. The nitrogen component is particularly beneficial for promoting overall plant growth, while the phosphorus enhances root development, flowering, and fruiting.
DAP is considered a complete fertilizer because it supplies two key nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) in one product. It is often used in soils that require both phosphorus and nitrogen, such as those used for growing cereals, grains, and vegetables.
Key Differences Between Triple Superphosphate and DAP
1. Nutrient Composition
The primary difference between Triple Superphosphate and DAP is their nutrient composition:
- Triple Superphosphate (TSP) is a pure phosphorus fertilizer, offering high levels of phosphorus but no nitrogen. This makes it ideal for soils that are deficient in phosphorus but already have sufficient nitrogen.
- Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a balanced fertilizer, providing both nitrogen and phosphorus. It is ideal for crops that require both nutrients for optimal growth.
This difference in composition makes each fertilizer better suited to specific types of crops and soil conditions.
2. Soil pH and Application
- TSP is most effective in acidic soils, where phosphorus is often less available. The high solubility of TSP makes it easy for plants to absorb phosphorus directly. However, if used in soils that are too alkaline, phosphorus from TSP may become locked in insoluble compounds, reducing its availability.
- DAP works well in neutral to slightly alkaline soils, where the ammonium content can help improve phosphorus availability by slightly acidifying the soil. It is also suitable for a variety of crops, including grains and vegetables.
Thus, TSP is better for acidic soils and phosphorus-deficient soils, while DAP is a more versatile fertilizer, effective across a wide range of soil types.
3. Crop Suitability
- TSP is commonly used for root crops such as carrots, potatoes, and onions, where a boost of phosphorus is needed for strong root development and early plant growth. It is also beneficial for legumes like peas and beans, which require phosphorus but are generally nitrogen-sufficient due to their nitrogen-fixing properties.
- DAP is often preferred for crops that require both phosphorus and nitrogen, such as corn, wheat, rice, and vegetables. The balanced nutrient profile of DAP supports overall plant growth, root development, and energy transfer during flowering and fruiting.
4. Effect on Soil pH
- TSP generally has a neutral to slightly acidic effect on soil pH. It is less likely to alter the pH of the soil significantly but is most effective in acidic conditions.
- DAP, due to its ammonium content, has a slight acidifying effect on soil. While this is beneficial in alkaline soils, it can cause the pH to drop over time, so it’s important to monitor soil pH regularly to prevent excessive acidity.

When to Use TSP vs DAP
The choice between Triple Superphosphate and DAP largely depends on your soil type, the crops you are growing, and the specific nutrient requirements of those crops.
1. When to Use Triple Superphosphate (TSP)
- For Acidic Soils: If your soil is acidic and lacks adequate phosphorus, TSP is the ideal choice. Its high phosphorus content will quickly supply the phosphorus your plants need for strong root development, flowering, and fruiting.
- For Phosphorus-Dependent Crops: If you are growing crops like root vegetables, legumes, or fruit trees that require phosphorus but do not need added nitrogen, TSP is a good option.
- When Nitrogen is Not Needed: If your soil already has sufficient nitrogen, there is no need to add more, and TSP will provide the needed phosphorus without excess nitrogen.
2. When to Use Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)
- For Neutral to Slightly Alkaline Soils: DAP is effective in neutral to slightly alkaline soils, where both nitrogen and phosphorus are needed to support plant growth.
- For Crops Needing Both Nitrogen and Phosphorus: If your crops require both phosphorus and nitrogen, such as cereals, grains, vegetables, and oilseeds, DAP is a balanced solution.
- For High-Phosphorus Crops: Crops such as corn, wheat, and rice, which require both a high level of phosphorus and nitrogen for optimal growth, will benefit from the combination of nutrients offered by DAP.
Conclusion: Which Fertilizer is Best for Your Crops?
Choosing between Triple Superphosphate and DAP depends on several factors, including your soil type, crop needs, and specific growth conditions.
- TSP is ideal for acidic soils that are deficient in phosphorus and is best for crops that need phosphorus but are already nitrogen-sufficient, such as root vegetables and legumes.
- DAP, being a complete fertilizer, is better suited for neutral to slightly alkaline soils where both nitrogen and phosphorus are required for robust plant growth. It is ideal for cereal crops, vegetables, and other crops that benefit from the dual nutrient supply.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision on which fertilizer to use, ensuring your crops get the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and optimal yield.





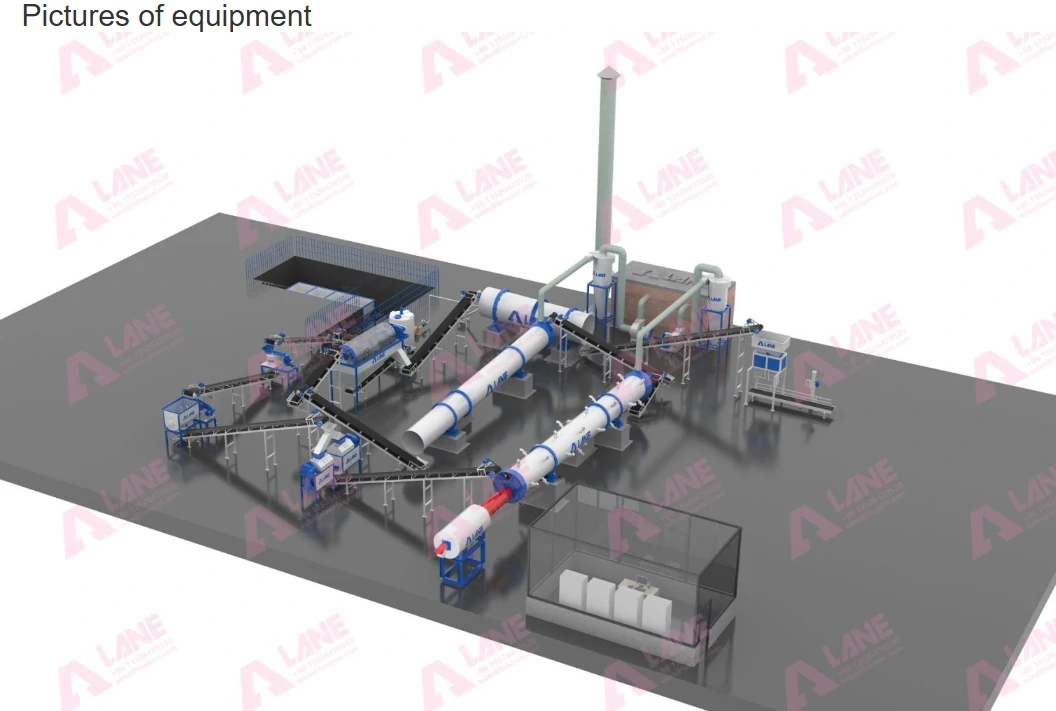
Send a message to us