Nourishing Crops, Sustaining Growth: The Role of Sulphate of Ammonium in Agriculture
As global agriculture faces the dual challenge of increasing food production while preserving the environment, the role of effective fertilizers has never been more critical. The LANE Group’s sulphate of ammonium production line produces sulphate of ammonium with high purity and good fertiliser efficiency. Among the fertilizers widely used to enhance soil fertility and promote plant growth, this stands out for its versatility and efficiency. This nitrogen-rich compound is particularly valued for its ability to provide essential nutrients that support healthy crop development and sustained agricultural productivity.
In this article, we will explore the various roles of sulphate of ammonium in agriculture, its benefits, application methods, and its contribution to sustainable farming practices.
What is Sulphate of Ammonium?
Sulphate of ammonium (also known as ammonium sulphate, chemical formula: (NH₄)₂SO₄) is a nitrogen-based fertilizer that supplies two key nutrients to crops:

- Nitrogen (N): Essential for vegetative growth, nitrogen promotes leaf development, chlorophyll production, and overall plant vigor.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur plays a crucial role in enzyme function, protein synthesis, and improving the plant’s resistance to environmental stresses.
The combination of these two nutrients makes sulphate of ammonium highly effective in addressing nitrogen and sulfur deficiencies in the soil, resulting in healthier and more productive crops.
How Sulphate of Ammonium Works in the Soil
Sulphate of ammonium functions by delivering nitrogen in the ammonium form, which is readily available for plant uptake. Nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll, all of which are essential for photosynthesis and plant growth. As nitrogen helps stimulate vegetative growth, sulphate of ammonium is commonly used during the early stages of crop development when rapid leaf and stem growth is crucial.
Additionally, the sulfur content of ammonium sulphate contributes to the formation of certain amino acids and vitamins that enhance plant metabolism. Sulfur also plays an essential role in building resistance to pests and diseases, improving the overall health and quality of crops.
Sulphate of ammonium is particularly beneficial in areas where soils are deficient in both nitrogen and sulfur, providing a dual nutrient solution that is cost-effective and efficient.
Key Benefits of Using Sulphate of Ammonium
a. Reliable Nitrogen Source

One of the primary advantages of sulphate of ammonium is its role as a stable and reliable source of nitrogen. Unlike nitrate-based fertilizers, which can be prone to leaching and runoff, ammonium nitrogen is less likely to be lost through water movement in the soil. This makes sulphate of ammonium an excellent option for maintaining nitrogen levels in areas with high rainfall or irrigation.
b. Improved Soil Acidity Control

Ammonium Sulphate can also help manage soil pH. Because ammonium undergoes a conversion process (nitrification) that releases hydrogen ions, it has an acidifying effect on the soil. This makes it particularly useful in soils with high pH (alkaline soils), where the slight acidification can improve nutrient availability and boost plant growth.
c. Sulfur Supplementation

In addition to nitrogen, crops require sulfur for the formation of key enzymes and proteins. Sulphate of ammonium is an effective source of sulfur, addressing sulfur deficiencies in the soil and enhancing the efficiency of nitrogen use. This leads to healthier crops and improved yields, particularly in sulfur-deficient regions.
d. Compatibility with Other Fertilizers

Ammonium Sulphate is compatible with a wide range of fertilizers, making it an excellent component in custom fertilizer blends. It can be mixed with other nutrients like potassium or phosphate fertilizers, allowing farmers to address multiple soil deficiencies in a single application.
e. Versatile Application Methods
The versatility of Ammonium Sulphate allows it to be applied through various methods, including direct soil application, fertigation (application through irrigation), or as a component in liquid fertilizers. This flexibility makes it easy to integrate into different farming systems and crop cycles.
Application Methods of Sulphate of Ammonium
To maximize the effectiveness of sulphate of ammonium, proper application methods are essential. Here are some common techniques used by farmers:
a. Broadcast Application

One of the most widely used methods is broadcasting, where the fertilizer is evenly spread across the soil surface before planting or after crops are established. This method ensures that the nitrogen and sulfur are distributed throughout the field, promoting uniform crop growth.
b. Banding
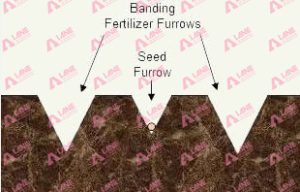
In banding, sulphate of ammonium is applied in narrow strips either beside or below the seed. This method is particularly effective for row crops like corn, wheat, or cotton, as it places the fertilizer close to the root zone, where it is readily accessible for plant uptake.
c. Fertigation
Fertigation involves applying fertilizers through irrigation systems, allowing the nutrients to be delivered directly to the plant’s root zone. Sulphate of ammonium is well-suited for fertigation due to its high solubility, ensuring that nutrients are efficiently distributed across the field while reducing the risk of leaching.
d. Top Dressing
Top dressing refers to the application of sulphate of ammonium after crops have emerged, typically during key growth stages. This method provides a timely nitrogen and sulfur boost, ensuring that crops continue to grow vigorously throughout their development.
Role in Sustainable Farming Practices
As agriculture moves toward more sustainable practices, sulphate of ammonium is playing a key role in promoting environmentally friendly farming. Here’s how it contributes to sustainable agriculture:
a. Reducing Nitrogen Losses
One of the significant environmental concerns with nitrogen fertilizers is the loss of nitrogen to the environment, either through volatilization (ammonia gas release) or leaching into groundwater. Sulphate of ammonium minimizes these losses by delivering nitrogen in the ammonium form, which is less susceptible to volatilization and leaching, especially in cooler soils.
b. Supporting Soil Health
The slow-release nature of ammonium nitrogen allows for steady, long-term plant nutrition without overloading the soil with excess nitrogen. Combined with the sulfur component, this results in healthier soils that can support productive crops season after season.
c. Improved Nutrient Use Efficiency
Sulphate of ammonium enhances the efficiency of nutrient use by addressing multiple nutrient deficiencies at once. This reduces the need for additional fertilizer applications, conserving resources and lowering input costs for farmers.
d. Compatibility with Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage, a method that reduces soil disturbance, is increasingly used to preserve soil structure and reduce erosion. Sulphate of ammonium can be easily integrated into conservation tillage systems, as it can be applied either on the surface or directly into the soil with minimal disruption.
Challenges and Solutions in Using Sulphate of Ammonium
While sulphate of ammonium offers many benefits, there are some challenges associated with its use. Here are a few common challenges and how farmers can address them:
a. Soil Acidification
The acidifying effect of sulphate of ammonium, while beneficial in alkaline soils, can lead to soil acidity over time if not managed properly. Farmers should conduct regular soil tests to monitor pH levels and, if necessary, apply lime to balance soil acidity.
b. Potential Nitrogen Overapplication
As with any nitrogen-based fertilizer, overapplication of sulphate of ammonium can lead to nutrient imbalances or runoff. To avoid this, farmers should follow recommended application rates based on soil tests and crop requirements.
Conclusion
Sulphate of ammonium is a valuable tool in modern agriculture, providing crops with essential nitrogen and sulfur while contributing to healthier soils and more sustainable farming practices. Its versatility, efficiency, and environmental benefits make it a preferred choice for farmers looking to optimize crop growth and productivity.
By incorporating sulphate of ammonium into balanced fertilization programs, farmers can achieve higher yields, improve crop quality, and reduce their environmental impact. As agriculture continues to evolve, this fertilizer will remain an essential part of sustainable crop management.





Send a message to us