How to Produce Single Super Phosphate Fertilizer
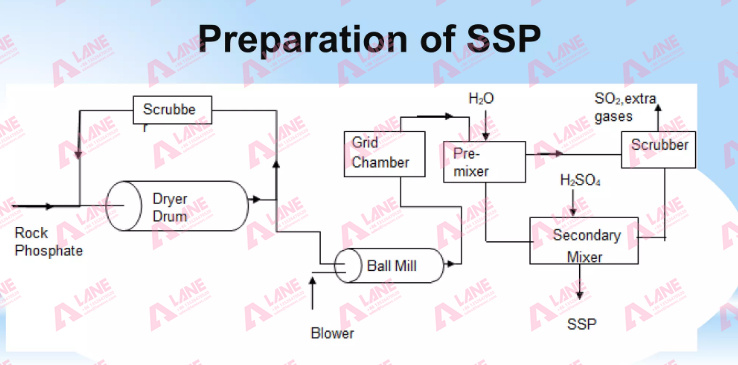
Single Super Phosphate (SSP) is one of the most commonly used phosphatic fertilizers in agriculture. It is produced by treating rock phosphate with sulfuric acid, which results in a highly effective source of phosphorus for plants. This fertilizer improves soil fertility and promotes healthy plant growth. In this article, we’ll discuss the step-by-step process of producing Single Super Phosphate fertilizer and the equipment required for each stage.
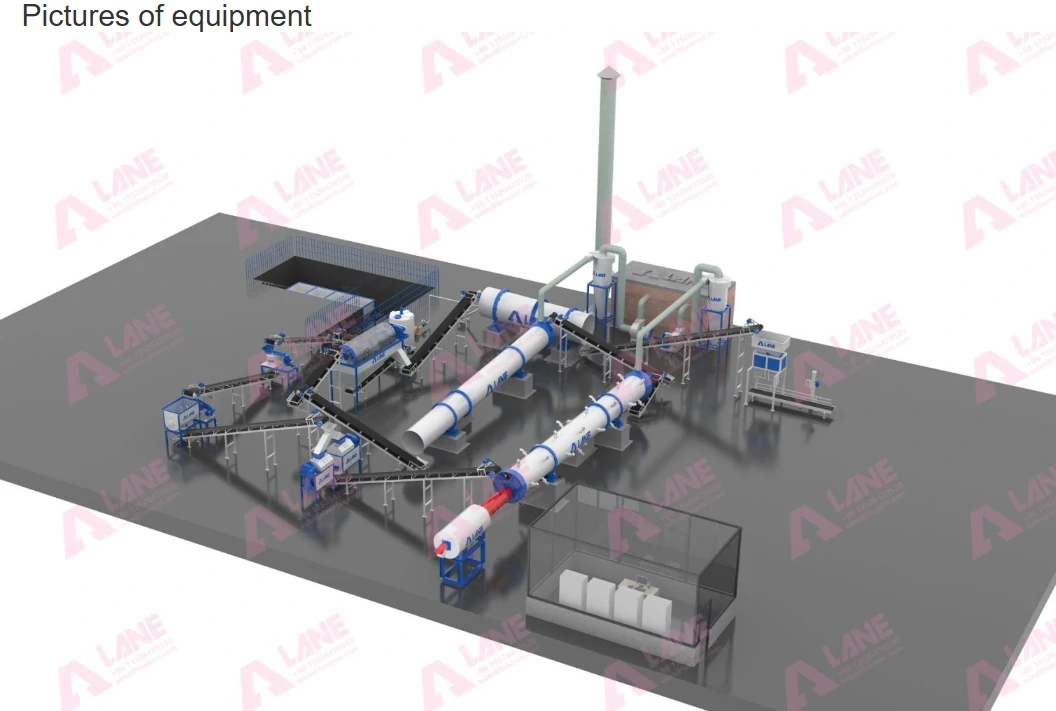
Equipment Needed:
- Granulator: A rotary drum or pan granulator is used to form the granules.
- Dryer: After granulation, the product is dried to remove excess moisture and make it suitable for storage.
- Screening Equipment: Granules are screened to separate any fines or oversized particles, ensuring uniform size.
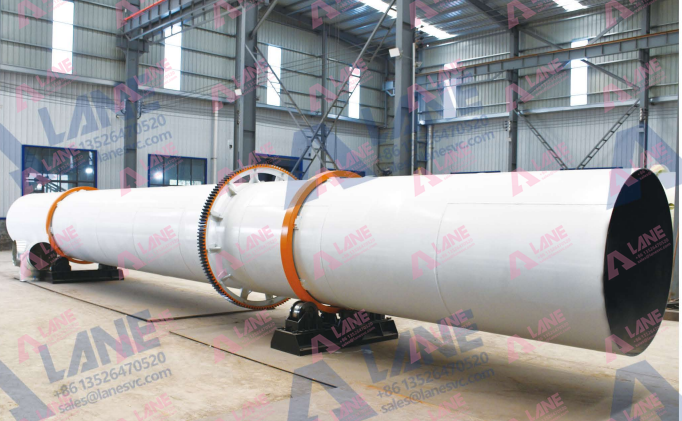
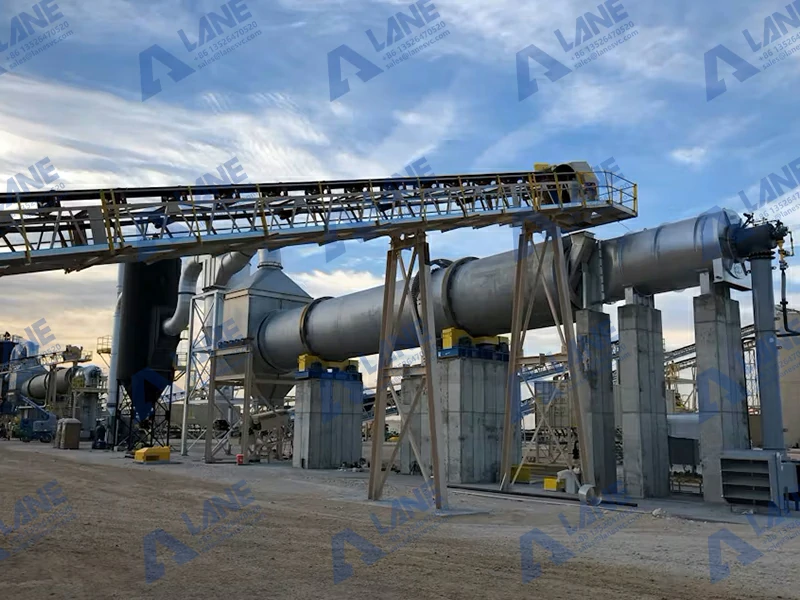
4. Drying and Cooling
After granulation, the SSP fertilizer granules need to be dried and cooled to ensure they do not clump together during storage. The drying process also reduces the moisture content, making the fertilizer more stable.
Key Steps:
- Drying: The granules are dried using a rotary drum dryer or fluidized bed dryer.
- Cooling: After drying, the granules are cooled to room temperature using a cooling system.
Equipment Needed:
- Rotary Drum Dryer: Used for drying the granules.
- Cooling System: Typically a cooling drum or air-cooling system is used to lower the temperature of the granules.
5. Packaging and Storage
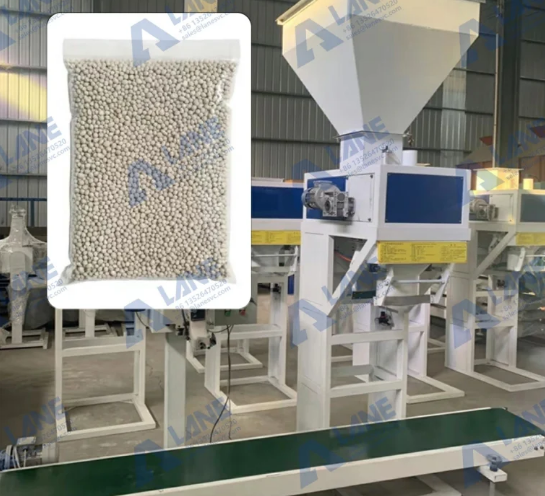

Once the SSP fertilizer has been dried and cooled, it is ready for packaging. The granules are weighed, packed into bags, and sealed for shipment. The packaging ensures that the fertilizer remains dry and free from contaminants during transport and storage.
Key Steps:
- Weighing: The final product is weighed to ensure each bag contains the correct amount of fertilizer.
- Packaging: The fertilizer is packed into bags of various sizes, depending on the requirements of the customer.
- Sealing: The bags are sealed to protect the fertilizer from moisture.
Equipment Needed:
- Automatic Packaging Machines: These machines weigh, fill, and seal the bags.
- Conveyors: Used to transport the bags to the storage area.
6. Quality Control
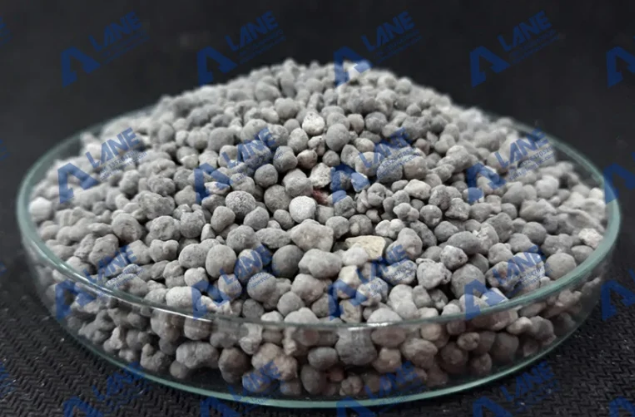

Quality control is an essential part of the SSP fertilizer production process. Samples of the final product are tested for nutrient content, moisture levels, and physical characteristics to ensure they meet the required specifications.
Key Quality Tests:
- Phosphorus Content: Ensuring that the fertilizer contains the right amount of phosphorus (usually 16-20%).
- Moisture Content: Ensuring that the fertilizer is not too wet, which could affect its storage stability.
- Granule Size: The size of the granules should be uniform for easy application.
Equipment Needed:
- Laboratory Testing Equipment: Used to measure nutrient content, moisture levels, and other physical properties.
Conclusion
Producing Single Super Phosphate fertilizer is a highly efficient process that involves mixing phosphate rock with sulfuric acid to produce phosphoric acid, which is then granulated and dried to form the final product. The production of SSP fertilizer is essential for improving soil fertility and providing plants with the necessary nutrients for growth. By understanding the key steps and the equipment involved, producers can ensure high-quality fertilizer production that meets the needs of modern agriculture.
Whether you’re setting up a new fertilizer plant or optimizing an existing one, paying attention to each stage of the process will help maximize the efficiency and quality of the SSP fertilizer you produce. The right equipment and attention to detail are crucial for ensuring that your fertilizer product is effective, safe, and beneficial to the environment.






Send a message to us