Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines: The Hidden Force Behind Global Food Security
Phosphate fertilizers are a cornerstone of modern agriculture, playing a critical role in the cultivation of crops that feed billions of people around the world. At the heart of this essential agricultural process are Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines, which transform raw phosphate rock into the nutrient-rich fertilizers that help sustain global food production. These production lines are the unsung heroes of agriculture, ensuring that soils are replenished with the phosphorus needed to maintain high crop yields and food security.
In this article, we explore how phosphate fertilizer production lines operate, their significance in global food security, and the technological advancements that are shaping the future of phosphate fertilizer manufacturing.
The Role of Phosphorus in Agriculture

Phosphorus is one of the three essential macronutrients for plant growth, alongside nitrogen and potassium. It plays a crucial role in various plant processes, including root development, energy transfer, and flowering. Without an adequate supply of phosphorus, crops cannot reach their full potential, resulting in reduced yields and compromised food production.
However, phosphorus is not readily available in many soils, which is why phosphate fertilizers are so critical. Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines ensure that this essential nutrient is delivered to farmers in a form that plants can absorb, enabling them to grow healthy and productive crops.
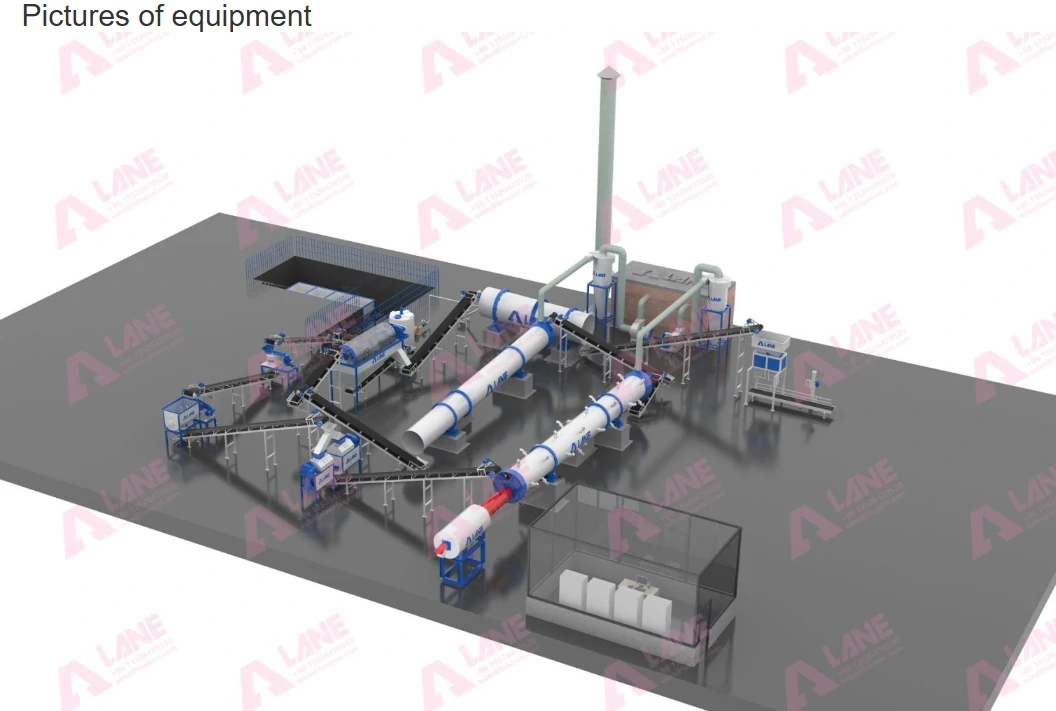
The Phosphate Fertilizer Production Process

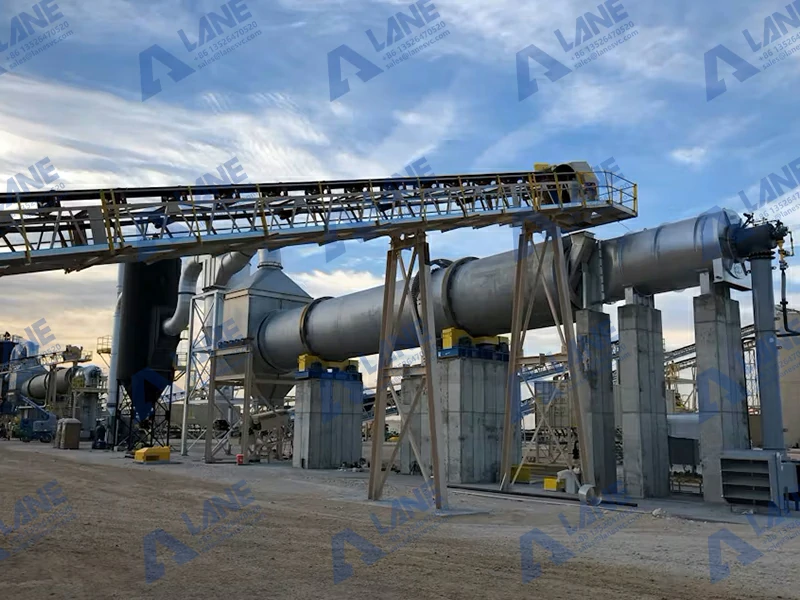
The journey of phosphate fertilizer production begins with the extraction of phosphate rock from mines. These rocks contain high concentrations of phosphorus, but they must undergo several processes before they can be converted into usable fertilizer. The transformation from raw rock to finished product takes place in Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines, which include several key stages:
a. Crushing and Grinding
The first step in phosphate fertilizer production is the crushing and grinding of phosphate rock. This process increases the surface area of the material, making it easier to process in subsequent stages. The finely ground phosphate rock is then prepared for the chemical reactions that will convert it into a usable form.
b. Acid Treatment
After crushing, the phosphate rock is treated with sulfuric acid in a process known as acidulation. This chemical reaction produces phosphoric acid, a key ingredient in phosphate fertilizers. The acidulation process also generates byproducts such as gypsum, which is often used in construction or soil conditioning.
The phosphoric acid produced in this step is then concentrated and purified, ensuring that it meets the quality standards required for fertilizer production.
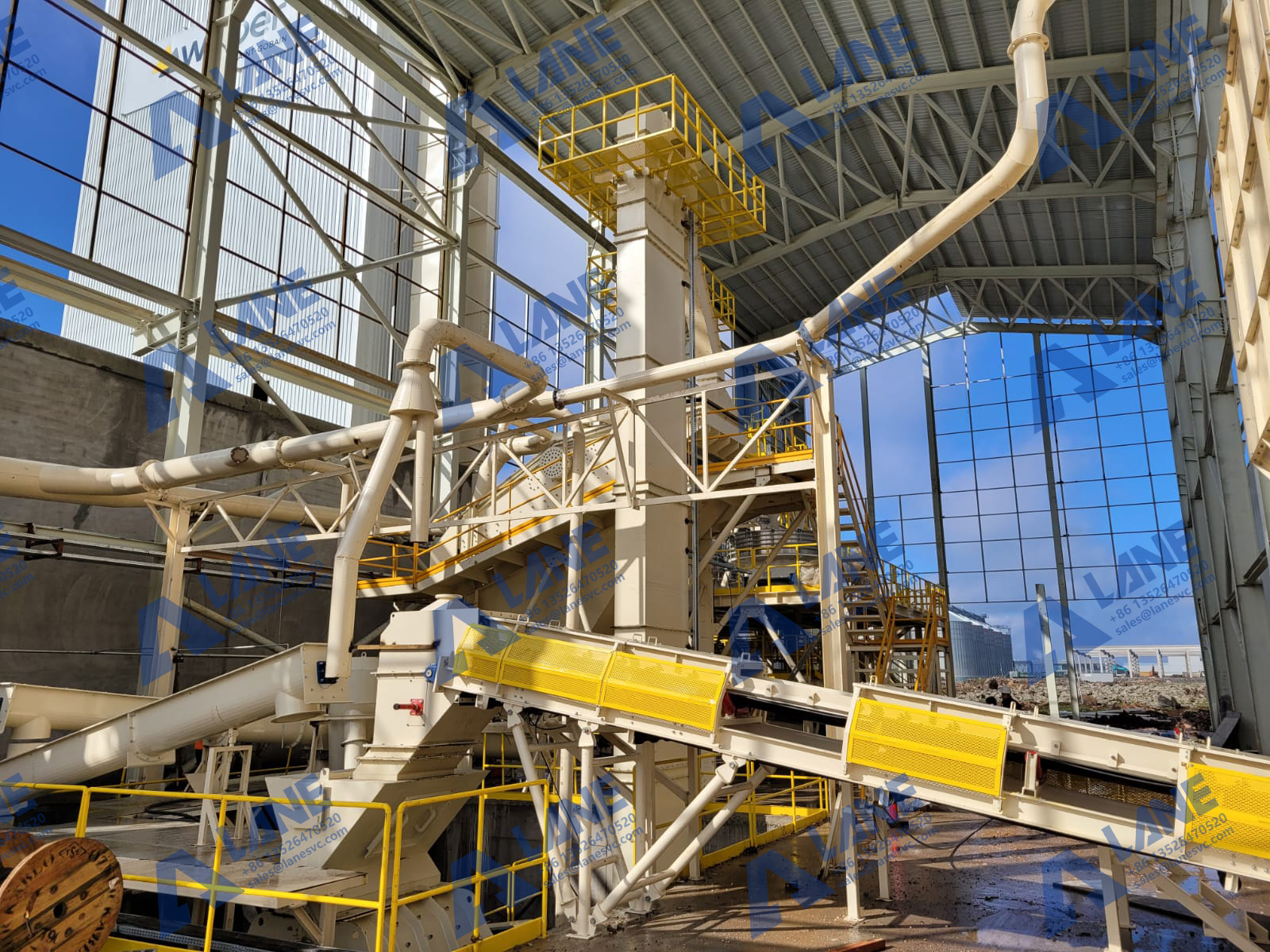
c. Granulation and Drying
Once the phosphoric acid is ready, it is mixed with other nutrients, such as ammonia or potassium, to create different types of phosphate fertilizers, including diammonium phosphate (DAP) and monoammonium phosphate (MAP). The mixture is then granulated, forming small, uniform granules that are easy to apply to fields.
The granules are dried to remove excess moisture, improving their stability and shelf life. After drying, the fertilizer is cooled and screened to ensure that the granules are the correct size for efficient application.
d. Quality Control and Packaging
The final stage in the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line is quality control. Fertilizers are tested to ensure they meet industry standards for nutrient content and granule size. Once they pass quality control, the fertilizers are packaged for distribution to farmers worldwide.
The Global Impact of Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines
Phosphate fertilizer production is a global industry, with major production centers in countries like Morocco, China, and the United States. These production lines are critical to ensuring that farmers around the world have access to the phosphorus they need to grow crops. Without phosphate fertilizers, many soils would become depleted of phosphorus, leading to lower yields and a decrease in global food production.
The significance of Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines cannot be overstated. By supplying phosphorus to agricultural systems, they help maintain high levels of crop productivity, enabling farmers to meet the growing demand for food as the global population continues to rise.
The Connection Between Phosphate Fertilizers and Food Security

Food security depends on a reliable and consistent food supply, which in turn relies on the availability of essential agricultural inputs like fertilizers. Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines play a vital role in this system by ensuring that farmers can maintain healthy, fertile soils that support high crop yields.
In regions where soils are naturally deficient in phosphorus, access to phosphate fertilizers is especially important. Without these fertilizers, farmers would struggle to produce enough food to feed local populations, leading to increased hunger and malnutrition. This Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line makes phosphate fertilizers a critical tool in the fight against food insecurity, particularly in developing countries where agriculture is the primary source of food and income.
Technological Advancements in Phosphate Fertilizer Production

As the demand for phosphate fertilizers continues to grow, so does the need for more efficient and sustainable production methods. Recent technological advancements in Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines are helping to improve both the efficiency and environmental sustainability of phosphate fertilizer manufacturing.
a. Energy Efficiency
One area of focus is improving the energy efficiency of phosphate fertilizer production. Traditional production methods are energy-intensive, but new technologies are being developed to reduce energy consumption. These advancements help lower the cost of production while also reducing the carbon footprint of fertilizer manufacturing.
b. Waste Management and Recycling
Phosphate fertilizer production generates several byproducts, such as gypsum, which can create disposal challenges. However, modern production lines are increasingly finding ways to recycle and reuse these byproducts, turning waste into valuable resources. For example, gypsum can be used in the construction industry or as a soil conditioner, reducing waste and contributing to a circular economy.
c. Precision Agriculture Integration
Another exciting development is the integration of phosphate fertilizers with precision agriculture technologies. By using data from soil sensors and GPS-guided equipment, farmers can apply phosphate fertilizers more accurately, ensuring that crops receive the nutrients they need while minimizing waste and runoff. This not only improves crop yields but also reduces the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Challenges and the Future of Phosphate Fertilizer Production
Despite the critical importance of phosphate fertilizers, the industry faces several challenges. One of the most pressing is the finite nature of phosphate rock reserves. Phosphate is a non-renewable resource, and there are concerns about the long-term availability of high-quality phosphate rock.
To address this issue, researchers are exploring alternative sources of phosphorus, such as recycling phosphorus from wastewater and agricultural residues. These innovations could help reduce the industry’s reliance on mined phosphate rock and ensure a more sustainable supply of phosphorus for future generations.
Conclusion
LANE Phosphate Fertilizer Production Lines are the hidden force behind global food security, transforming raw phosphate rock into the fertilizers that sustain modern agriculture. As the world’s population continues to grow, the importance of these production lines will only increase. By investing in new technologies and sustainable practices, the phosphate fertilizer industry can continue to play a vital role in feeding the world while protecting the environment for future generations.





Send a message to us