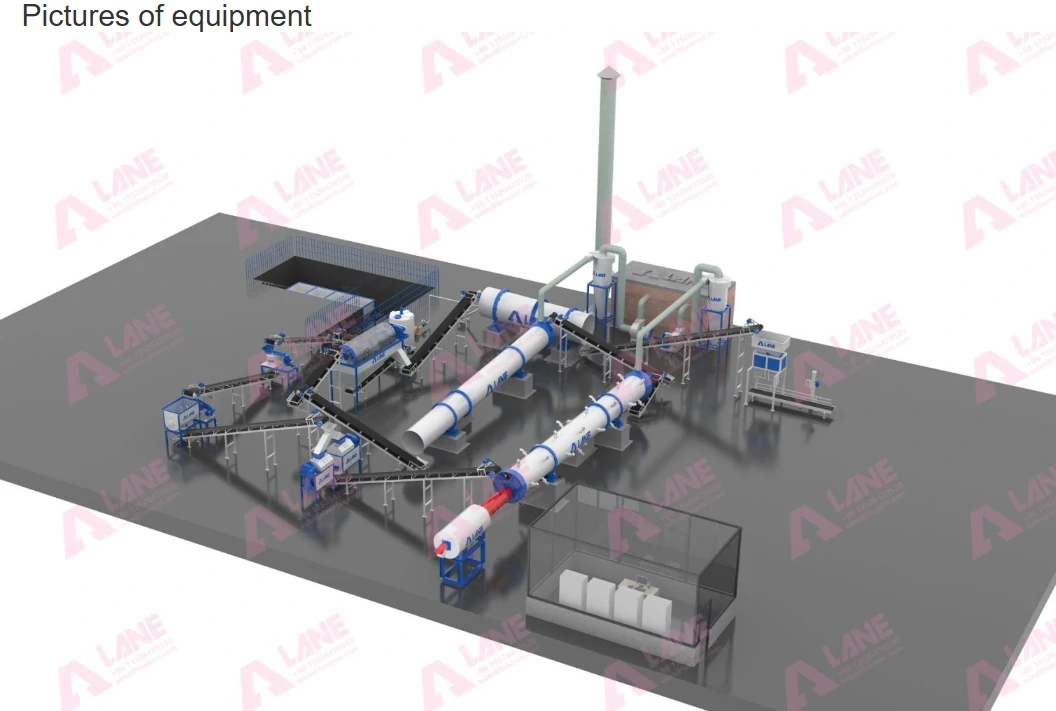
Phosphate Fertilizer Production
The production of phosphate fertilizer is a vital component of global agriculture, enabling farmers to grow crops that feed billions of people. Phosphorus, one of the three essential macronutrients for plants, is crucial for root development, flowering, and fruit production. As the demand for food increases, so does the need for efficient phosphate fertilizer production. At the heart of this process is the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line, a complex series of steps that transforms raw phosphate rock into nutrient-rich fertilizer.
In this article, we will explore the journey of phosphate rock from its extraction to its conversion into the fertilizers that are critical for modern agriculture. We will examine the key stages of the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line, the technologies involved, and the economic and environmental impacts of this process.
The Importance of Phosphate in Agriculture

Phosphorus is an essential nutrient that promotes healthy root systems, enhances water usage, and supports plant growth. However, it is not naturally abundant in most soils, which makes phosphate fertilizers indispensable for farmers around the world. Phosphate fertilizers supply the necessary phosphorus in a form that plants can readily absorb.
The growing global population and the increasing need for food security have placed a greater emphasis on maximizing crop yields, and phosphorus is a critical element in achieving this. Without sufficient phosphorus, crops suffer from poor growth, weak root systems, and reduced yields, which can have devastating effects on food supply chains.
Extracting Phosphate Rock: The Starting Point

The Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line begins with the extraction of phosphate rock from mining operations. Phosphate rock is found in deposits around the world, with significant reserves in countries like Morocco, China, and the United States. This rock is rich in phosphates, the raw material needed to produce fertilizers.
Once mined, the phosphate rock is transported to a processing facility, where it undergoes initial crushing and grinding. This step reduces the size of the rock, making it easier to handle and process in the subsequent stages. Efficient crushing and grinding are essential for maximizing the surface area of the rock, ensuring that the phosphorus can be extracted more effectively.
The Chemical Transformation: Phosphoric Acid Production
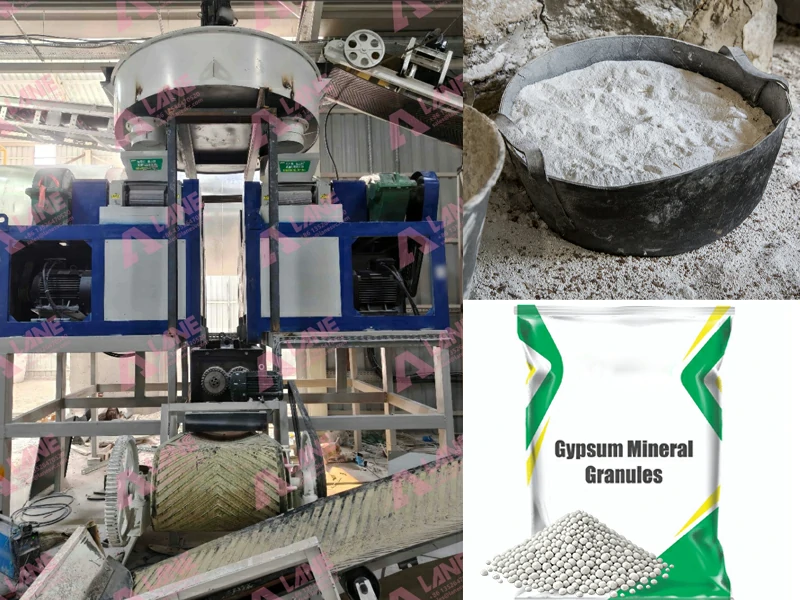
The next stage in the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line involves the conversion of phosphate rock into phosphoric acid, the primary ingredient in phosphate fertilizers. This is achieved by reacting the crushed phosphate rock with sulfuric acid in a chemical reactor. The reaction produces phosphoric acid and calcium sulfate (gypsum) as a byproduct.
This process, known as the wet-process method, is the most common method used in phosphate fertilizer production. The resulting phosphoric acid is then concentrated and purified to produce the high-quality acid required for fertilizer manufacturing. The efficiency of this stage is critical, as it determines the overall yield of phosphorus from the phosphate rock.
Granulation: Turning Acid into Fertilizer

After producing phosphoric acid, the next step in the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line is to convert it into a solid form that can be easily transported and applied to fields. This is where the granulation process comes into play.
Granulation involves mixing the phosphoric acid with other compounds, such as ammonia or potassium, to create different types of phosphate fertilizers. For example, combining phosphoric acid with ammonia produces diammonium phosphate (DAP) or monoammonium phosphate (MAP), two of the most widely used phosphate fertilizers.
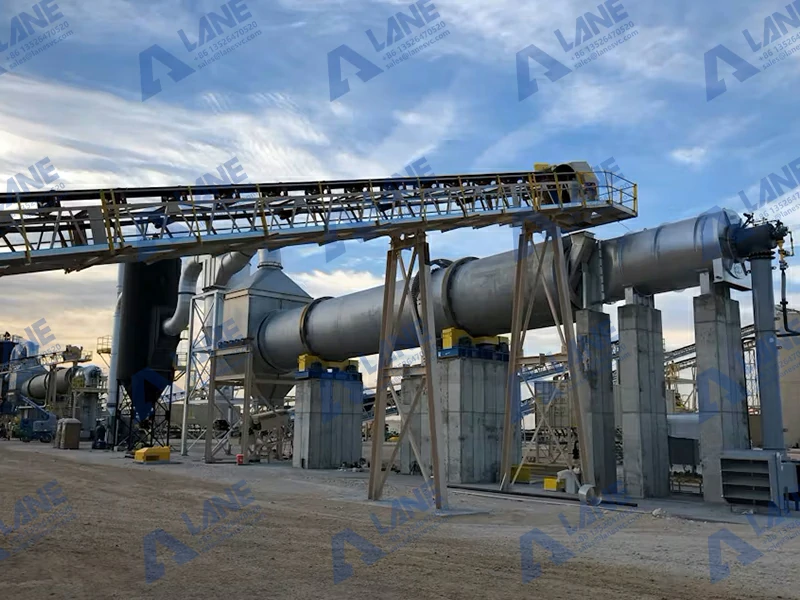
The granulation process uses advanced machinery to form the mixture into granules, which are then dried, cooled, and screened to ensure uniform size and quality. These granules are easy to store and transport and provide a slow-release source of phosphorus to crops, ensuring efficient nutrient uptake.
Quality Control and Packaging

One of the most critical aspects of the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line is quality control. Throughout the production process, fertilizers are tested to ensure they meet strict quality standards. Factors such as phosphorus content, granule size, and moisture levels are carefully monitored to guarantee that the final product performs optimally in the field.
Once the fertilizers pass quality control checks, they are packaged for distribution. Depending on the end use, fertilizers can be packaged in bulk for commercial farming operations or in smaller bags for retail sale to individual farmers. Efficient packaging ensures that the fertilizer reaches its destination in optimal condition, ready to be applied to crops.
Environmental Considerations in Phosphate Fertilizer Production
The production of phosphate fertilizers is a resource-intensive process that requires careful management of environmental impacts. Mining phosphate rock can result in habitat disruption, water usage, and waste generation, while the chemical processing of the rock produces emissions and byproducts such as gypsum.
However, advancements in Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line technologies are helping to mitigate these environmental concerns. Many phosphate production plants are now investing in more sustainable practices, such as recycling waste products, reducing water consumption, and capturing emissions. For instance, the gypsum byproduct can be used in the construction industry, reducing waste and providing an additional revenue stream.
Moreover, precision agriculture technologies are improving the application of phosphate fertilizers, reducing the risk of over-fertilization and minimizing nutrient runoff into water bodies, which can cause environmental issues like eutrophication.
Economic Impact and Global Trade
The global phosphate fertilizer industry is a multi-billion-dollar sector, with significant economic implications for both producing and consuming countries. Phosphate fertilizers are essential for ensuring food security in many regions, especially in countries with phosphorus-deficient soils.
Countries with large phosphate rock reserves, such as Morocco, dominate the global phosphate fertilizer trade, exporting significant quantities to regions with high demand, such as Asia and Europe. The economic importance of phosphate fertilizers extends beyond agriculture, as it creates jobs in mining, manufacturing, and distribution, contributing to the overall economic health of many nations.
The Future of Phosphate Fertilizer Production
As global demand for food continues to rise, the role of the Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line will only grow in importance. However, with the finite nature of phosphate rock reserves, the industry faces challenges in ensuring the long-term availability of phosphorus. Innovations in phosphorus recycling, such as recovering phosphorus from wastewater, are being explored as potential solutions to reduce reliance on mined phosphate rock.

Additionally, the development of more sustainable production technologies and the adoption of precision farming practices will be critical in meeting future demand while minimizing the environmental impact of phosphate fertilizer production.
Conclusion
The LANE Phosphate Fertilizer Production Line is a complex and essential process that transforms phosphate rock into the fertilizers that drive global agricultural productivity. From mining and chemical processing to granulation and packaging, each stage plays a critical role in ensuring that farmers have access to the nutrients they need to grow healthy crops.
As the world’s population continues to grow, phosphate fertilizers will remain a key tool in ensuring food security. By investing in innovative technologies and sustainable practices, the phosphate fertilizer industry can continue to meet the challenges of feeding a growing world while protecting the environment for future generations.





Send a message to us