Fertilizer Production Machinery: The Key to Addressing the Global Food Crisis
The world is currently experiencing a severe food crisis, with alarming reports from the United Nations indicating that over 820 million people are undernourished and more than 2 billion suffer from micronutrient deficiencies. This crisis is being driven by a range of factors, including climate change, population growth, and the shrinking availability of arable land. One critical factor exacerbating this crisis is the limited access to sufficient quantities of affordable fertilizer. As demand for fertilizers rises, global supply chains have struggled to keep pace, leading to shortages that severely impact agricultural productivity. To address these issues, fertilizer production machinery is increasingly recognized as a crucial solution to boosting fertilizer availability, improving agricultural output, and ultimately mitigating the world food crisis.
The Growing Demand for Fertilizers
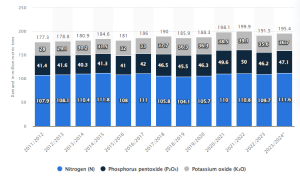
Fertilizers play an essential role in modern agriculture by providing vital nutrients that enhance soil fertility and boost crop yields. As the global population continues to grow, food demand has risen sharply, and with it, the need for fertilizers to sustain agricultural productivity. However, the global fertilizer trade has become unstable, with countries imposing tariffs, export restrictions, and other trade barriers that have disrupted supply chains. This instability has led to significant shortages, especially in developing regions, where small-scale farmers are unable to access the fertilizers they need to cultivate enough food to meet local demand.
To make matters worse, traditional chemical fertilizers contribute to soil degradation and environmental pollution, making it more important than ever to shift toward sustainable alternatives such as organic fertilizers. This is where fertilizer production machinery comes into play, offering scalable solutions that enable local production of high-quality fertilizers, both chemical and organic, at lower costs.
The Role of Fertilizer Production Machinery in Meeting Global Food Needs
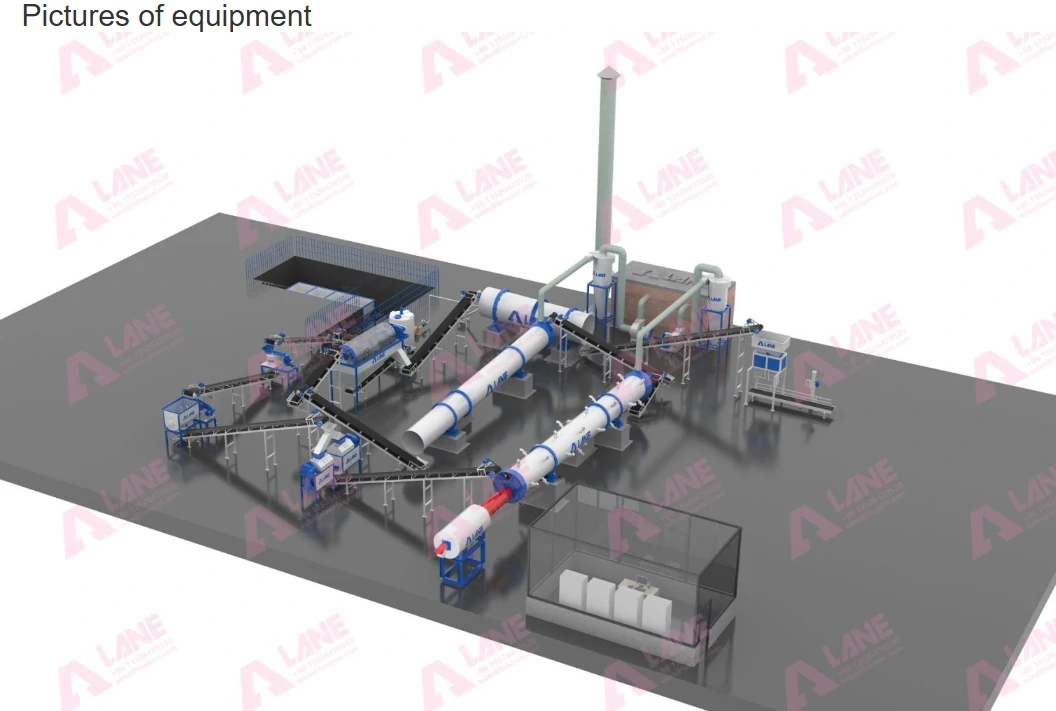
Fertilizer production machinery refers to a wide array of equipment designed to manufacture different types of fertilizers, including disc granulator machines, manure pellet machines, fertilizer granule-making machines, and organic fertilizer granulators. These machines are critical to the production process, transforming raw materials like manure, crop residues, and minerals into nutrient-rich fertilizers that improve soil health and plant growth.
By investing in advanced fertilizer production machinery, countries can localize fertilizer production, reducing dependence on volatile global supply chains. This localized production can be particularly beneficial for small-scale farmers who struggle with high fertilizer prices due to import tariffs and transportation costs. With access to affordable, locally-produced fertilizers, these farmers can increase their agricultural productivity, reducing poverty and improving food security in rural areas.
Moreover, machinery such as organic fertilizer granulators enables the production of eco-friendly fertilizers, which are better suited for long-term soil health. Organic fertilizers derived from composted waste or animal manure not only provide essential nutrients but also improve soil structure and biodiversity, contributing to sustainable farming practices.
Types of Fertilizer Production Machinery and Their Benefits
Several types of fertilizer production machinery are available, each serving a specific purpose in the fertilizer manufacturing process. These machines are integral to enhancing production capacity and efficiency, ensuring that farmers have a steady supply of fertilizers.
a. Disc Granulator Machines

Disc granulator machines are commonly used for producing granulated fertilizers by turning raw materials into uniform, round granules. This process improves the ease of handling, transportation, and application of fertilizers. Granulated fertilizers are preferred by many farmers due to their slow-release properties, which provide nutrients to plants over an extended period, reducing the need for frequent reapplication.
b. Manure Pellet Machines

Manure pellet machines are used to process animal manure into small, compact pellets that can be used as organic fertilizers. This machinery is vital for converting waste into a valuable resource, reducing the environmental impact of animal farming while promoting sustainable agriculture. These pelletized fertilizers are nutrient-rich and improve soil organic matter, making them ideal for enhancing soil fertility over time.
c. Fertilizer Granule Making Machines

Fertilizer granule-making machines are versatile, enabling the production of both organic and inorganic fertilizers. These machines can handle a variety of raw materials, including mineral compounds and agricultural waste. Their versatility allows farmers and producers to create tailored fertilizers that meet specific crop needs, improving the efficiency of nutrient delivery and enhancing crop yields.
d. Small-Scale Fertilizer Plants
Small-scale fertilizer plants incorporate several pieces of machinery to create a streamlined production process. These plants are ideal for local production, particularly in rural areas where large-scale industrial fertilizer plants are not feasible. Small-scale fertilizer plants can produce a range of fertilizers that meet the specific needs of local farmers, fostering food security at a grassroots level.
The Environmental Impact of Fertilizer Production Machinery
Beyond addressing food security, fertilizer production machinery also plays a critical role in promoting environmental sustainability. Traditional chemical fertilizers, while effective in boosting crop yields, often lead to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, organic fertilizers produced by machinery such as manure pelletizers or compost granulators are environmentally friendly. They reduce the need for synthetic chemicals and support long-term soil health by improving soil structure and increasing biodiversity.
By turning agricultural waste, such as crop residues or animal manure, into fertilizer, production machinery helps close the nutrient loop, preventing waste from being discarded in landfills or contributing to pollution. This circular economy approach not only reduces waste but also provides a renewable source of nutrients for agricultural use.
Economic and Social Benefits of Fertilizer Production Machinery
The economic and social benefits of adopting fertilizer production machinery are vast. For smallholder farmers, access to affordable fertilizers through localized production can improve crop yields, leading to higher income levels and reduced poverty. Fertilizer production machinery can also create jobs within rural communities, providing employment opportunities in manufacturing, distribution, and sales.
In addition, the availability of affordable and locally-produced fertilizers strengthens food security by ensuring that farmers can grow enough food to feed their communities. This is particularly important in regions where food insecurity is prevalent, and reliance on imported fertilizers is not sustainable in the long term.
Conclusion

The world food crisis is a complex issue driven by a variety of factors, but one of the key contributors is the lack of access to affordable, high-quality fertilizers. Fertilizer production machinery offers a scalable, sustainable solution by enabling the local production of both chemical and organic fertilizers. These machines not only improve soil health and crop yields but also support environmental sustainability and economic development in rural areas. By investing in fertilizer production machinery, governments and agricultural stakeholders can make significant strides toward alleviating the global food crisis and building a more resilient, food-secure future.





Send a message to us