Boost Effect of Phosphoric Acid in Agriculture
Phosphoric acid plays a crucial role in agriculture, primarily through its application in phosphate fertilizers. Understanding the effect of phosphoric acid can significantly enhance crop yields, improve soil health, and support sustainable farming practices. This article explores the benefits and mechanisms of phosphoric acid in agricultural systems, highlighting its importance in modern farming.
Phosphoric acid plays a crucial role in agriculture, primarily through its application in phosphate fertilizers. Understanding the effect of phosphoric acid can significantly enhance crop yields, improve soil health, and support sustainable farming practices. This article explores the benefits and mechanisms of phosphoric acid in agricultural systems, highlighting its importance in modern farming.
The Different Effect of Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid is primarily utilized in the production of phosphate fertilizers, such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP). These fertilizers are rich in phosphorus, one of the three essential macronutrients for plants. Phosphorus is vital for various physiological processes, including photosynthesis, energy transfer, and root development. The effect of phosphoric acid on crop growth is profound, as it ensures that plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal performance.
One of the primary advantages of phosphoric acid is its ability to increase phosphorus availability in the soil. In many agricultural soils, phosphorus can become immobilized or bound to soil particles, making it less accessible to plants. The application of phosphoric acid helps to release this bound phosphorus, making it more soluble and available for plant uptake. This enhanced availability is especially important in soils with high pH levels, where phosphorus tends to precipitate and become less soluble.
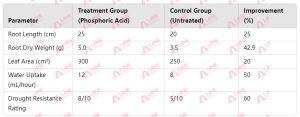
The effect of phosphoric acid extends beyond nutrient availability; it also enhances root development. Adequate phosphorus levels promote strong root systems, which are essential for nutrient and water absorption. Healthy root systems enable plants to withstand environmental stresses, such as drought and nutrient deficiencies. Consequently, the use of phosphoric acid can lead to improved crop resilience and overall growth.
Rootstalk Defenders
In addition to enhancing root systems, the effect of phosphoric acid is evident in its role in increasing flowering and fruiting. Phosphorus is critical during the reproductive stages of plant growth, influencing flower formation and fruit set. Research has shown that crops treated with phosphoric acid often exhibit increased flowering rates and higher fruit yields. This boost in reproductive success can significantly impact overall agricultural productivity, making phosphoric acid a valuable tool for farmers.
When applying phosphoric acid, various methods can be employed to maximize its benefits. Soil application is one of the most common techniques. Farmers can incorporate phosphoric acid into the soil before planting to ensure that phosphorus is readily available for seedlings. Broadcasting granular phosphate fertilizers containing phosphoric acid over the field is another effective method, allowing for even nutrient distribution.
Foliar application is also a viable option, particularly during critical growth stages. A diluted solution of phosphoric acid can be sprayed directly onto plant leaves, allowing for rapid absorption of phosphorus. This method can be particularly beneficial during flowering and fruiting, where plants require higher phosphorus levels for optimal development.

Determining the appropriate dosage of phosphoric acid is essential for maximizing its benefits. Soil testing is crucial to assess existing phosphorus levels and pH. Based on the results, farmers can tailor their application rates to meet specific crop requirements. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental issues, such as runoff and pollution. Therefore, adhering to local agricultural guidelines and consulting with agronomists can help ensure that farmers apply the correct amount of phosphoric acid.
Timing is another critical factor when using phosphoric acid. The ideal application period may vary depending on the crop type and growth stage. Applying phosphoric acid during soil preparation ensures that phosphorus is available for emerging seedlings. In contrast, foliar applications may be more effective during flowering or when plants show signs of nutrient deficiency.
While the effect of phosphoric acid is beneficial, safety precautions should be taken during handling. Farmers should wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, to avoid irritation. Proper storage is also essential; phosphoric acid should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials.
Environmental considerations are paramount when using phosphoric acid. Responsible application is crucial to minimize nutrient runoff, which can contaminate water bodies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Farmers should establish buffer zones around water sources and follow recommended application rates. Precision farming techniques can also help ensure accurate and efficient application of effect of phosphoric acid, reducing the risk of environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effect of phosphoric acid in agriculture is significant, contributing to improved nutrient availability, enhanced crop yields, and healthier soils. By understanding how to apply phosphoric acid effectively—through proper methods, dosage, and timing—farmers can harness its benefits to optimize agricultural productivity sustainably. As global food demand continues to rise, the role of phosphoric acid in enhancing crop production and ensuring food security will remain vital. With careful management and responsible use, phosphoric acid can help drive innovation and efficiency in modern agriculture, ultimately supporting sustainable farming practices for future generations.






Send a message to us