DAP vs TSP: A Manufacturing and Process-Based Comparison
When it comes to producing phosphate fertilizers, few comparisons are as relevant—or as revealing—as DAP vs. TSP. These two products dominate global markets, yet they represent very different approaches to delivering phosphorus to crops. While both contain high levels of P₂O₅, the similarities stop there. From chemical makeup and production methods to operational demands and market positioning, understanding the nuances between DAP vs. TSP is essential for manufacturers, investors, and agronomists alike.
Let’s dive into eight key differences that define this ongoing rivalry in fertilizer manufacturing.
Nutrient Composition – Why DAP and TSP Are Not Interchangeable?
The most immediate distinction in any discussion of DAP vs TSP lies in their nutrient profiles. Diammonium phosphate (DAP) delivers both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P₂O₅), typically around 18% N and 46% P₂O₅. In contrast, triple superphosphate (TSP) offers nearly the same level of phosphorus but contains no nitrogen at all.
This difference alone determines how each product is used in the field. Farmers applying DAP get two nutrients in one application, reducing labor and logistics. With TSP, growers must supplement nitrogen separately—a factor that influences everything from pricing to distribution strategies.
For manufacturers, this also shapes downstream flexibility. A plant built for DAP can’t easily switch to TSP—and vice versa. The choice isn’t just technical; it’s strategic.

Production Process – Neutralization vs Acidulation
One of the clearest divergences between DAP vs TSP emerges in how they’re made.
DAP begins with a precise neutralization reaction: ammonia gas reacts with phosphoric acid under tightly controlled conditions. This creates a slurry that feeds directly into granulation. Speed, temperature, and pH balance are critical. Any deviation can disrupt flow, cause clumping, or yield off-spec material. It’s a continuous, high-precision process.

TSP takes a slower, more straightforward path. Here, phosphate rock is mixed with phosphoric acid and allowed to cure over time. No ammonia involved. Once cured, the material moves to granulation and drying. While still requiring care, the process is less sensitive and easier to manage.
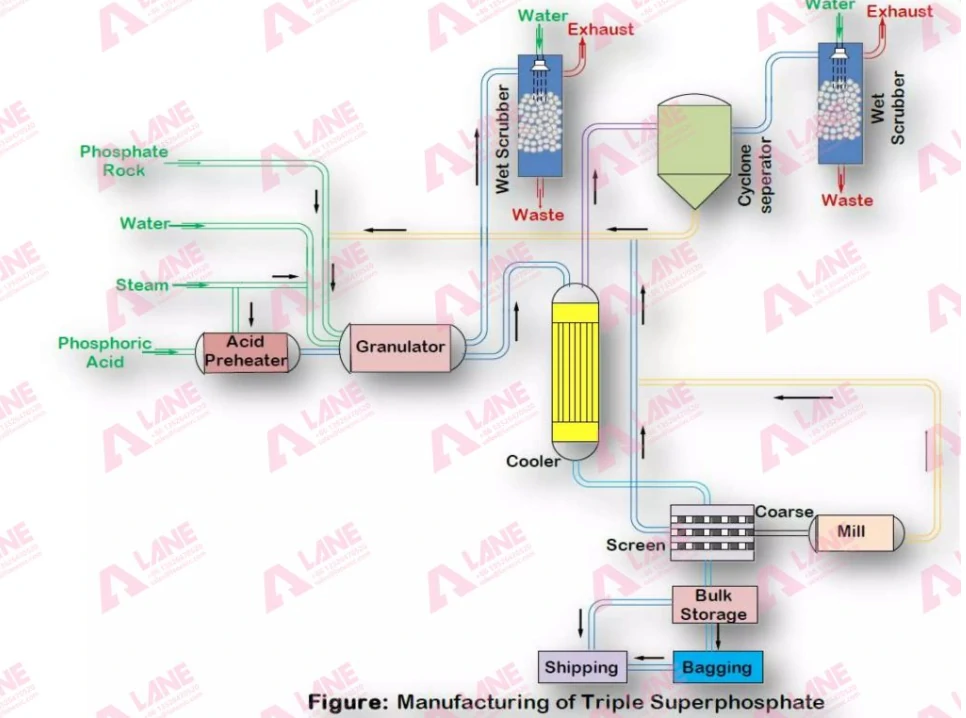
In short: DAP runs like a race car—fast, finely tuned, demanding. TSP drives like a reliable sedan—steady, predictable, low-maintenance.
Granulation Behavior – Sensitivity Makes All the Difference
Granulation performance further highlights why DAP vs TSP plants feel so different on the ground.
In DAP systems, moisture control is paramount. Too wet, and particles stick; too dry, and they won’t bind. Because the slurry comes straight from neutralization, inconsistencies propagate quickly—leading to uneven particle size or weak granules. Recycle rates often exceed 50%, increasing complexity.
TSP granulation, by contrast, is remarkably forgiving. Cured material behaves consistently, making moisture management simpler. Granule formation is stable, even under minor fluctuations. Many TSP lines operate with lower recycle loads and fewer adjustments—translating to smoother operations and less downtime.
Operators notice the difference: DAP requires constant vigilance; TSP allows room for error.
Equipment & Plant Design – Complexity Has a Price Tag
Compare a DAP facility to a TSP plant, and you’ll see engineering extremes.
DAP setups include ammonia storage tanks, pre-reactors, advanced scrubbers, and automated control rooms. Every component addresses safety, emissions, or precision. Dust and fluoride gases require robust treatment. Automation isn’t optional—it’s mandatory.
TSP plants, meanwhile, feature standard granulation drums, conveyor belts, and basic dust collectors. There’s nothing exotic about them. Maintenance teams handle fewer moving parts, and spare inventory stays lean.
The result? Capital costs for DAP can be double those of an equivalent TSP line. For budget-conscious developers, this gap narrows the field fast.
Operational Demands – High-Skill vs Low-Friction
Running a DAP plant demands expertise. Neutralization happens in minutes—delays risk solidification. Temperature, pH, and flow rates demand real-time monitoring. Even with automation, human judgment remains crucial.
TSP operations, while not simple, are generally more relaxed. Curing provides a buffer: mistakes can be corrected before granulation. Acidulation doesn’t require split-second decisions. Training takes days, not weeks. Turnover hurts less.
For regions with limited technical talent, this simplicity becomes a major advantage.
Environmental & Safety Records – Ammonia Changes Everything
Safety protocols differ dramatically when comparing DAP vs TSP.
Ammonia—the heart of DAP—is toxic, corrosive, and volatile. Leaks, spills, or improper handling pose serious risks. Plants must install closed-loop systems, emergency showers, and continuous emission monitors. Compliance adds cost, but skipping it invites disaster.
TSP avoids these dangers. Its primary concerns are dust and hydrogen fluoride—manageable with proper ventilation and baghouses. Workers face fewer hazards, insurance premiums stay lower, and communities breathe easier.
Environmental regulations increasingly favor lower-risk processes. As scrutiny grows, TSP gains appeal—even among large producers.
Market Applications – Compound vs Straight Fertilizer Strategies
Farmers do not always require both nitrogen and phosphorus at the same time. Soil analysis often reveals sufficient nitrogen levels while phosphorus remains limited. This is where DAP vs TSP becomes a practical decision. TSP is well suited for such conditions, as it can be blended with urea or potash to create customized fertilizer formulas based on specific soil needs.
In contrast, DAP functions as a ready-to-use starter fertilizer. It is widely applied in crops such as corn, wheat, and rice, where early root development is critical. By supplying nitrogen and phosphorus in a single product, DAP simplifies logistics and handling, often reducing transportation and storage complexity.
From a manufacturing perspective, DAP vs TSP selection should follow market demand. Regions that rely on tailored fertilizer blends tend to favor TSP production. Markets that prioritize simplicity and fast application often show stronger demand for DAP.
Economic Viability – Capital-Intensive vs Accessible Models
Finally, economics seal the fate of DAP vs TSPDAP commands higher prices per ton due to added value. But reaching that point requires heavy investment. Building a new DAP line could take years and millions of dollars. Ongoing expenses—ammonia, energy, skilled labor—cut into margins.
TSP offers faster returns. Lower startup costs, simpler operations, and access to local phosphate rock make it attractive for emerging producers. Even established firms choose TSP when expanding without straining finances.
Choosing Between DAP and TSP
There is no universal answer in the DAP vs TSP comparison. The choice depends on several factors, including raw material availability, market demand, investment capacity, and technical expertise.
DAP production offers higher product value and formulation flexibility. TSP production provides operational simplicity and lower technical risk.
Manufacturers should evaluate both technical and economic factors before selecting a production route in DAP vs TSP.
Final Thought: Choose Based on Reality, Not Hype
There’s no universal winner in the DAP vs TSP debate. Each fits specific contexts.
Ask yourself:
- Do I have affordable ammonia?
- Is my market asking for compound fertilizers?
- Can I justify the capital expense?
- How important is operational simplicity?
Answer honestly, and the path forward becomes clear. Whether you’re planning a new facility or optimizing an existing one, understanding these eight differences gives you a solid foundation for smarter decisions.
Ultimately, the best choice isn’t just about chemistry—it’s about matching technology to reality.
Ready to choose the right fertilizer solution? Contact LANE today to learn more about .
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520





Send a message to us