DAP Fertilizer Production Line: Process, Equipment, and Industrial Design
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) is one of the most important phosphorus-rich fertilizers in modern agriculture, widely used to improve soil fertility and crop yields due to its high nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P₂O₅) content. DAP fertilizer production line is an integrated industrial system that converts raw materials into finished granules through controlled chemical reactions, granulation, drying, cooling, and packaging. Understanding how a DAP production line works, what equipment it includes, and what factors influence its design is necessary for manufacturers and plant operators.
What Is a DAP Fertilizer Production Line?
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) fertilizer is produced through a controlled chemical reaction between phosphoric acid and ammonia, resulting in a compound that typically contains about 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus pentoxide, making it one of the most widely manufactured phosphate fertilizers worldwide; this production methodology is described in the International Chemical Information Service (ICIS) Diammonium Phosphate methodology, which explains global production and trading standards for DAP.
A DAP fertilizer production line is a comprehensive manufacturing solution designed for large-scale industrial production of diammonium phosphate fertilizer. In general, the process begins with the preparation and handling of phosphoric acid and ammonia, followed by neutralization to form a reaction slurry, granulation, moisture removal, and final product finishing steps. Modern lines are built for efficiency, product uniformity, and compliance with environmental standards.
Industrial Context and Market Demand
With global fertilizer demand continually rising, DAP remains a cornerstone for nitrogen-phosphorus supply in agricultural systems. The composition of DAP (commonly around 18% nitrogen and 46% P₂O₅) makes it valuable for balanced crop nutrient programs, especially where plant growth requires both readily available nitrogen and phosphorus. The effective production of DAP fertilizer relies on carefully engineered production systems backed by process control and industrial automation.
DAP Fertilizer Production Process
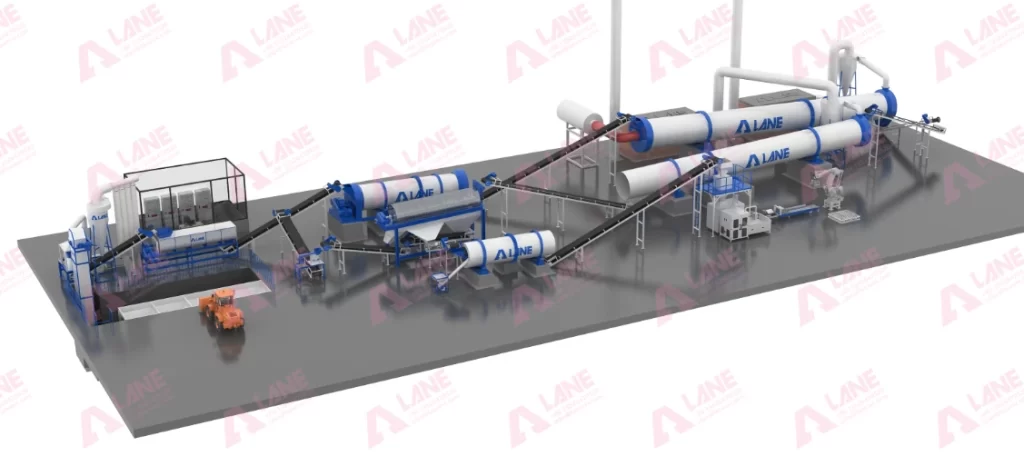
The typical DAP production process can be broken down into several core stages that must be optimized to ensure product quality and operational stability:
1. Raw Material Preparation
The essential raw materials for a DAP fertilizer production line are phosphoric acid and ammonia. These materials must be stored, handled, and pre-conditioned in a way that supports consistent reaction conditions. High-quality storage systems and controlled feeding mechanisms help minimize contamination and moisture variations — both of which can affect the chemical neutralization stage.
2. Neutralization Reaction
At the heart of DAP fertilizer production Line is the neutralization reaction between phosphoric acid and ammonia. In this controlled environment, ammonia reacts with the acid to form an ammonium phosphate slurry. The molar ratio must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired nutrient composition and minimize free excess reactants. In practice, this is done in a neutralization tank or reactor where temperature, pH, and reactant feed rates are monitored in real time.
3. Granulation
Following neutralization, the ammonium phosphate slurry is fed into a granulator. The granulation stage transforms the slurry into solid granules of uniform size and shape, which are critical for ease of application, storage stability, and nutrient release consistency. Typical granulators include rotary drum systems, disc granulators, or other industrial granulation machines that provide controlled residence time and mechanical agitation.
4. Drying and Cooling
The freshly granulated DAP fertilizer contains moisture that must be reduced before storage and shipment. A drying system — usually a rotary dryer — removes moisture via heated airflow, after which the granules are cooled to ambient temperature to prevent caking and maintain particle integrity. Proper drying and cooling are essential to achieve stable moisture content and physical strength.
5. Screening and Packaging
Once dried and cooled, the product is screened to separate finished granules from fines or oversized particles. Consistency in particle size ensures even nutrient distribution and better handling characteristics. Qualified products are then packaged in bags or bulk containers for storage or distribution.
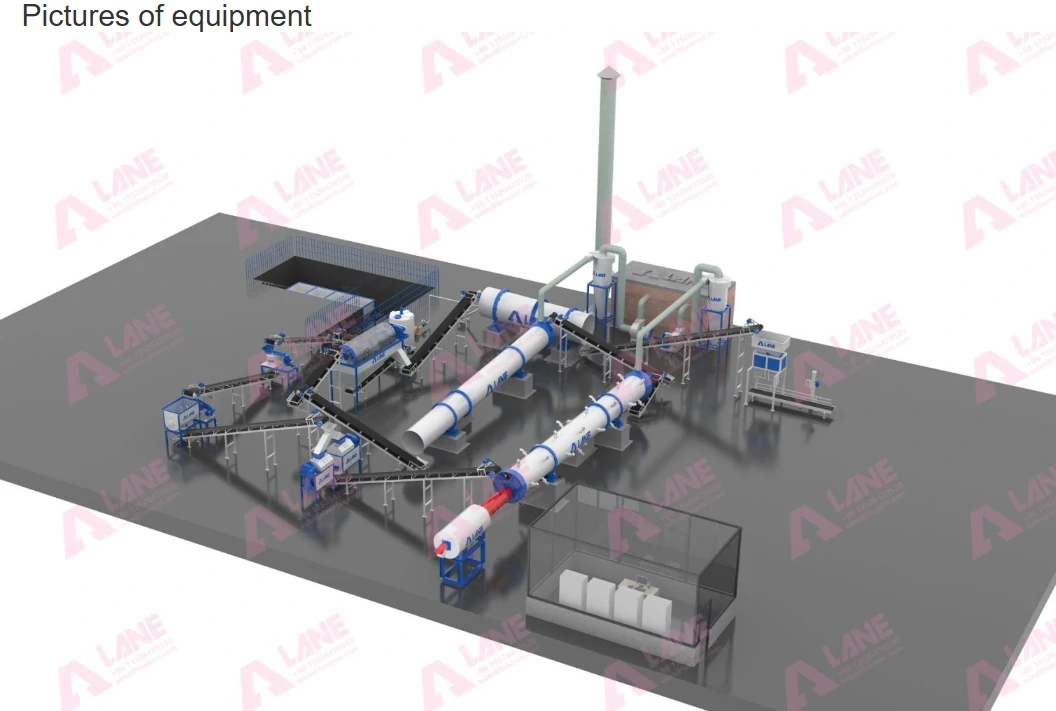
Core Equipment in a DAP Fertilizer Production Line

A complete DAP fertilizer production line integrates multiple specialized machines. Each plays a crucial role in processing raw materials into finished granules.
Neutralization/Reaction Systems
The reactor or neutralization tank provides a controlled space for phosphoric acid and ammonia to react efficiently, often with automated monitoring of temperature, pH, and feed ratios to maintain consistent chemistry.
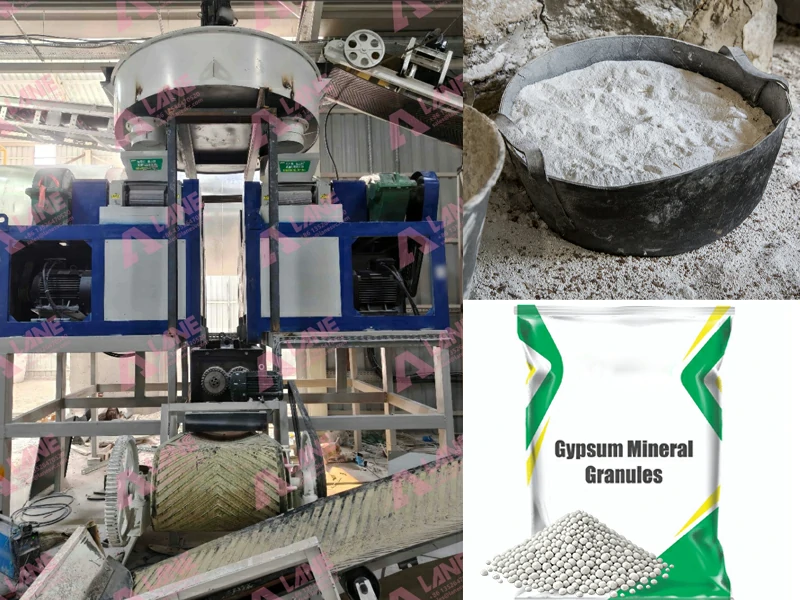
Granulators
Granulators are among the most important pieces of equipment in a production line. They ensure uniform granule size and improved nutrient distribution. Industrial granulators may include rotary drums or customized spray granulators, depending on production capacity.
Drying and cooling systems work together to remove moisture and stabilize the granules. Rotary dryers reduce water content, while cooling systems prevent particle agglomeration and help maintain storage quality.
High-precision screens separate qualified products from off-size material, improving final quality. Packaging machines automate weighing, bagging, and sealing, ensuring efficient throughput and minimized labor cost.
Design Considerations for DAP Fertilizer Production Lines
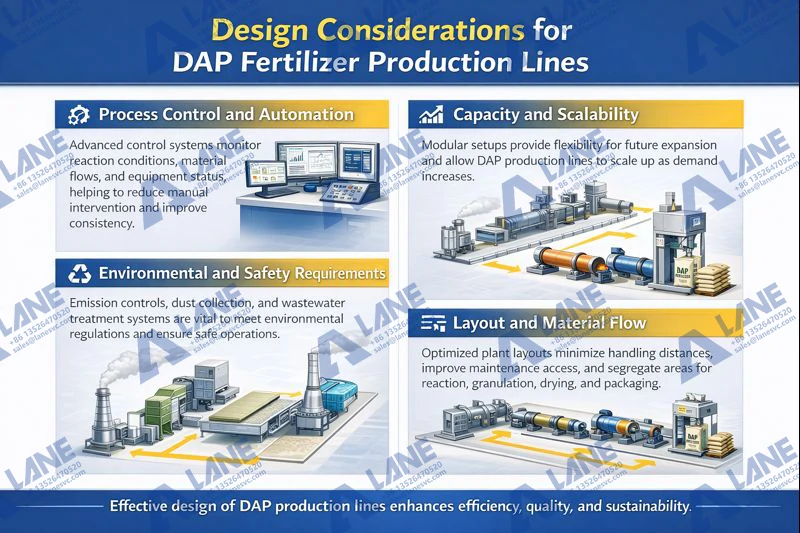
Designing an efficient DAP production line requires careful planning and engineering considerations that impact long-term stability, product quality, and operational efficiency.
Process Control and Automation
Advanced control systems are critical for monitoring reaction conditions, material flows, and equipment status. Automation helps reduce manual intervention, improve consistency, and lower operational risk.
Capacity and Scalability
Production capacity is a primary consideration when planning a DAP fertilizer production line. Manufacturers must balance projected output demand against investment and operational costs. Modular setups allow capacity expansion without excessive initial investment.
Environmental and Safety Requirements
Environmental compliance is increasingly important. Modern lines may incorporate emissions controls, dust collection, and wastewater treatment systems to meet national and international standards, reducing environmental impact and ensuring sustainable operations.
Layout and Material Flow
A well-optimized plant layout reduces material handling distances, improves safety, and enhances maintenance access. Clear segregation of reaction, granulation, drying, and packaging areas contributes to smoother production flow and reduced downtime.
Advantages of DAP Fertilizer
DAP fertilizer is valuable for its nutrient profile and agronomic effectiveness. With a balanced composition of nitrogen and phosphorus, it supports early plant growth, root development, and overall crop vigor. These properties make DAP a preferred choice in many cropping systems around the world.
In comparing phosphate fertilizers such as TSP and DAP, differences in nutrient content and application can be better understood by examining their production backgrounds and chemical compositions. This comparison is discussed in our article on TSP and DAP fertilizer differences and applications, which provides context on how design and manufacturing influence performance.
Industrial Applications of a DAP Fertilizer Production Line

Beyond basic production, modern DAP Fertilizer Production Line support large-scale commercial manufacturing and can be integrated into diversified phosphate fertilizer portfolios. Some advanced systems enable formula flexibility (e.g., adjusting N-P₂O₅ ratios) and environmentally compliant operations with energy-saving and emission-reduction technologies.
Conclusion
A DAP fertilizer production line is an vital industrial investment for manufacturers aiming to produce high-quality diammonium phosphate fertilizer efficiently and sustainably. With advanced equipment, robust control systems, and careful design, plants can achieve consistent product quality, meet regulatory requirements, and support agricultural productivity worldwide.





Send a message to us