Challenges in DAP Fertilizer Manufacturing and How to Overcome Them
09/29/2024
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) is one of the most widely used fertilizers in the world, providing essential nutrients that enhance plant growth and agricultural productivity. However, the manufacturing process of DAP fertilizer presents several challenges that can impact both production efficiency and environmental sustainability. Understanding these challenges and exploring potential solutions is crucial for manufacturers aiming to produce high-quality fertilizers while addressing the growing global demand for food.
Implementing rigorous testing protocols for incoming raw materials can further enhance product quality and production efficiency. This proactive approach enables manufacturers to adjust their processes based on the characteristics of the raw materials, ensuring consistent output.
- Adopt Sustainable Practices and Technologies

To comply with environmental regulations and reduce the impact of DAP Fertilizer Manufacturing on the environment, manufacturers should invest in sustainable practices and technologies. This includes adopting cleaner production techniques that minimize waste and emissions. For instance, using closed-loop systems can help capture and recycle ammonia emissions, reducing environmental harm.
Additionally, integrating byproduct management strategies can turn waste products like gypsum into valuable resources, such as building materials or soil amendments. This not only reduces waste but also contributes to a more circular economy within the agricultural sector.
- Enhance Energy Efficiency

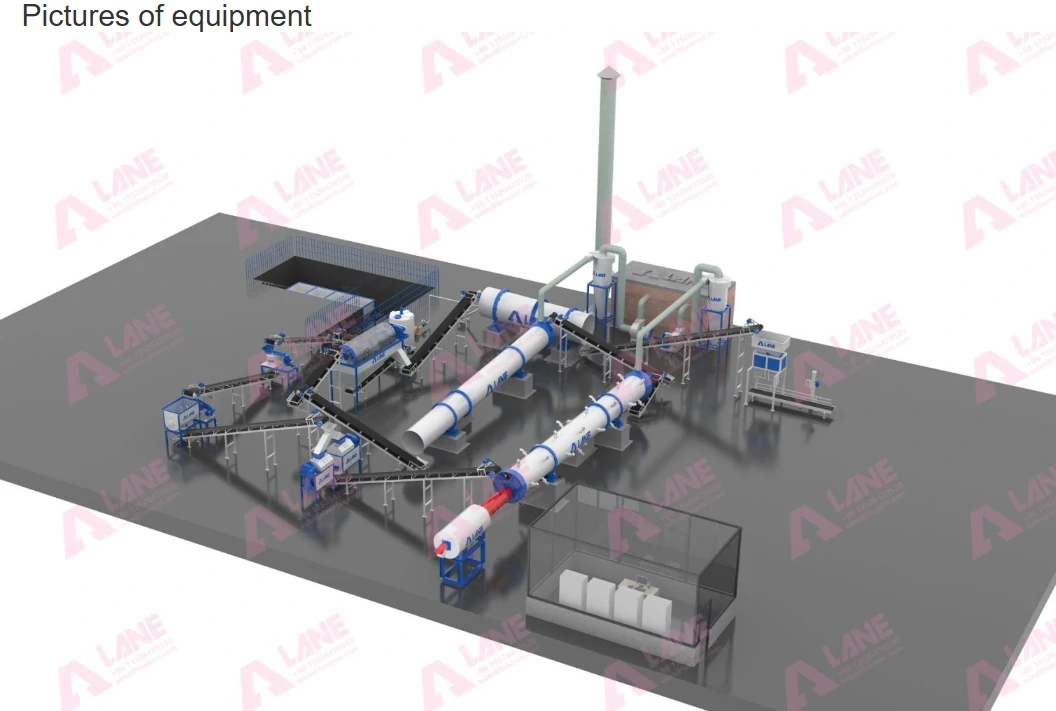
Dynamic Batching System
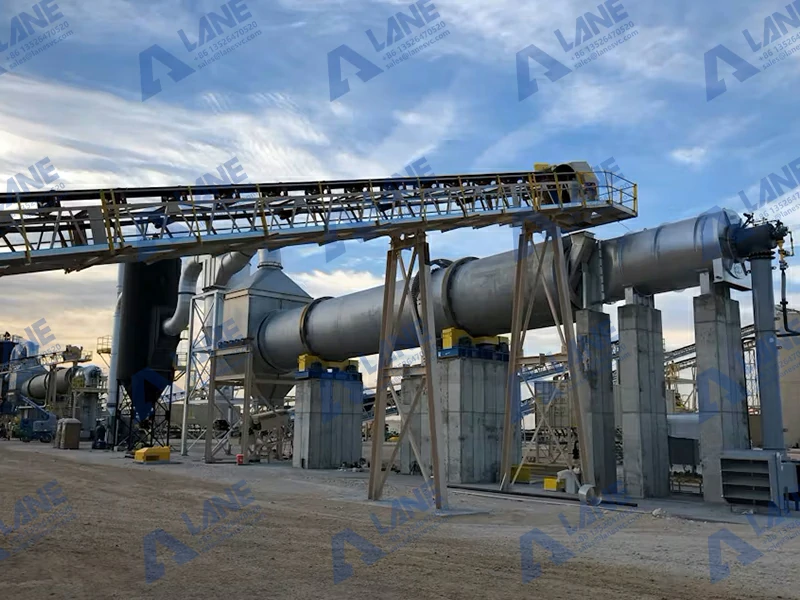
Improving energy efficiency is crucial for reducing production costs and minimizing the environmental footprint of DAP fertilizer manufacturing. Manufacturers can invest in energy-efficient machinery and technologies, such as advanced heat recovery systems and optimized process controls, to reduce overall energy consumption.
Implementing process automation can also enhance efficiency by reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of human error. Automated systems can monitor energy use in real-time, allowing manufacturers to make adjustments that optimize energy consumption throughout the production process.
- Implement Robust Quality Control Measures
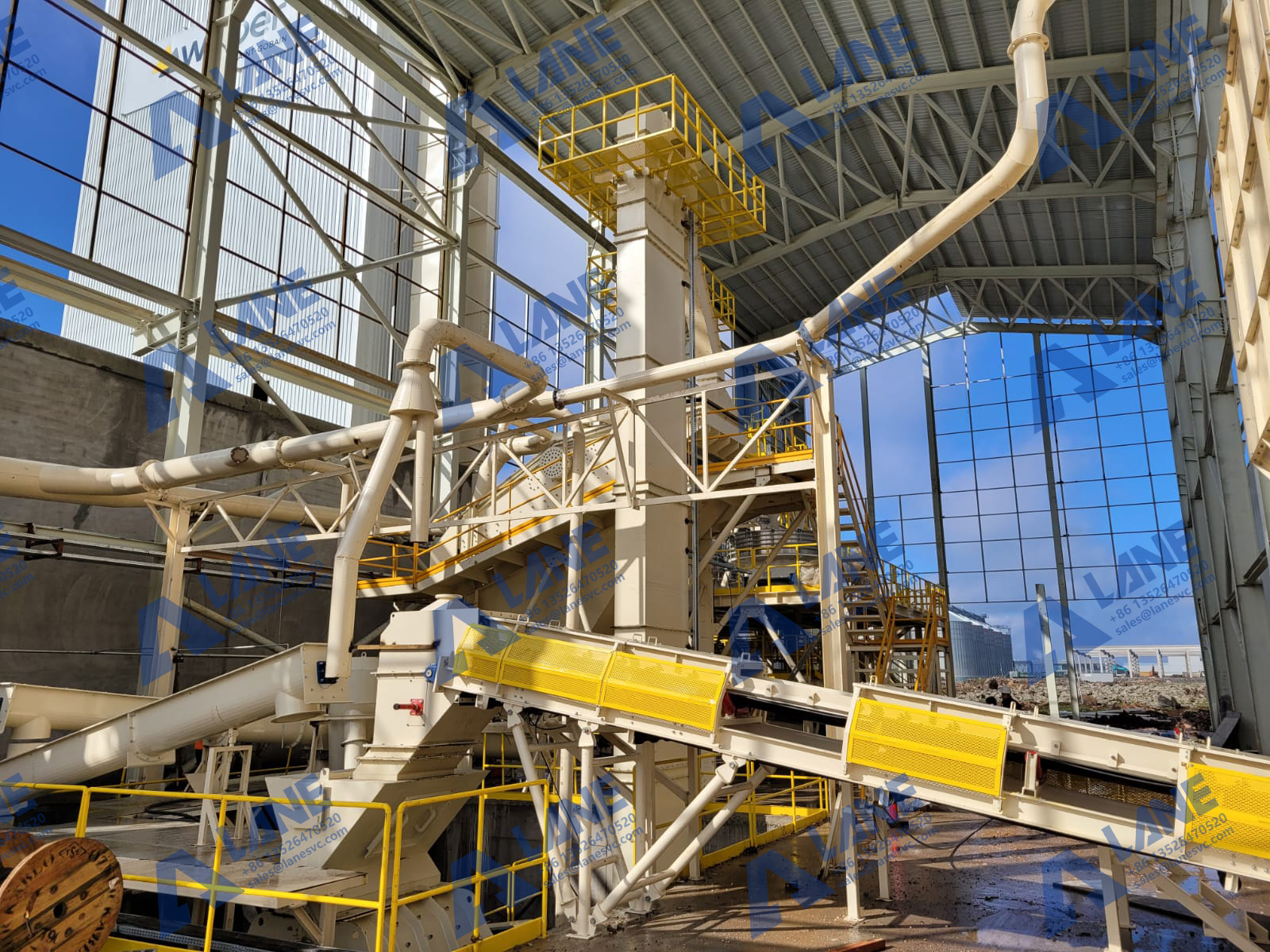
To ensure consistent DAP Fertilizer Manufacturing quality and improve production efficiency, manufacturers should establish comprehensive quality control measures throughout the production process. This includes regular monitoring and testing at various stages, from raw material inspection to final product evaluation.
By employing modern quality assurance technologies, such as data analytics and machine learning, manufacturers can identify trends and address potential issues before they impact production. This proactive approach can help maintain product integrity, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance overall competitiveness in the market.
Conclusion
The challenges associated with DAP Fertilizer Manufacturing are significant, but they are not insurmountable. By investing in raw material sourcing, adopting sustainable practices, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing robust quality control measures, manufacturers can overcome these obstacles and produce high-quality fertilizers that meet the needs of modern agriculture.
As the global demand for food continues to rise, the importance of efficient and sustainable DAP fertilizer production cannot be overstated. By addressing the challenges in manufacturing, companies can contribute to global food security while promoting environmental sustainability in the agricultural sector. The future of DAP fertilizer manufacturing lies in embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and committing to sustainable practices that benefit both producers and consumers alike.







Send a message to us