How Calcium Chloride Production Lines Support Agriculture and Beyond
Calcium chloride, a versatile chemical compound, plays a significant role in agriculture, manufacturing, and infrastructure maintenance. Known for its hygroscopic properties, calcium chloride absorbs moisture and serves various purposes, from soil improvement to crop preservation. The efficient operation of a Calcium Chloride Production Line ensures a consistent supply of this essential compound, supporting agricultural practices and several industries worldwide.
This article explores how calcium chloride production lines work, their impact on agriculture, and their applications in industries beyond farming.
The Role of Calcium Chloride in Agriculture

In agriculture, Calcium Chloride Production Line provides multiple benefits that improve soil health, enhance crop quality, and support efficient farming practices. One of its primary uses is addressing calcium deficiencies in the soil, which can lead to problems like blossom-end rot in crops such as tomatoes and peppers. By providing soluble calcium, calcium chloride helps plants absorb essential nutrients more efficiently, promoting healthier growth and better yields.
Farmers also use calcium chloride to manage soil salinity. In regions where soil contains excessive sodium, calcium chloride replaces sodium ions, improving soil structure and reducing compaction. This creates a better environment for root development and water absorption, resulting in more resilient crops.
The compound also serves as an effective foliar spray, improving fruit firmness and shelf life. When applied to apples, citrus fruits, or vegetables, calcium chloride reduces post-harvest losses by preventing diseases and maintaining product quality during storage and transportation.
Overview of Calcium Chloride Production Line

How Calcium Chloride Production Lines Work
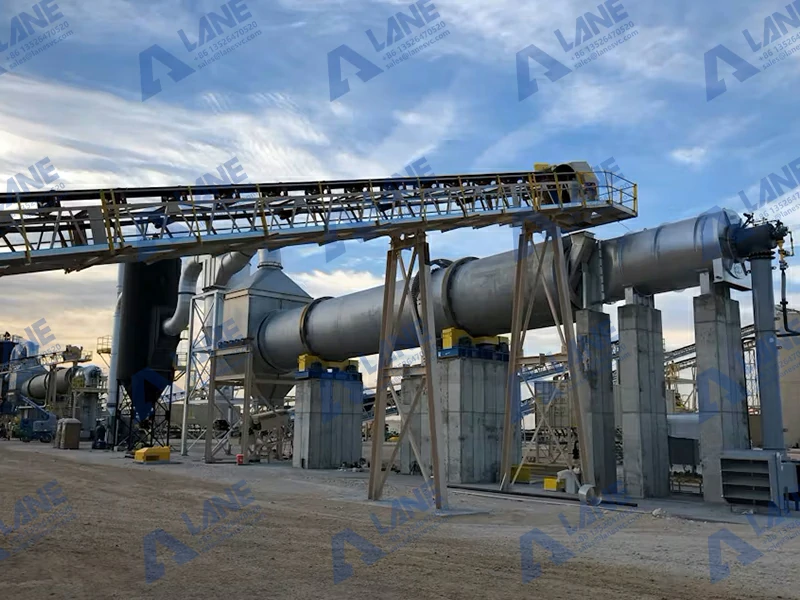
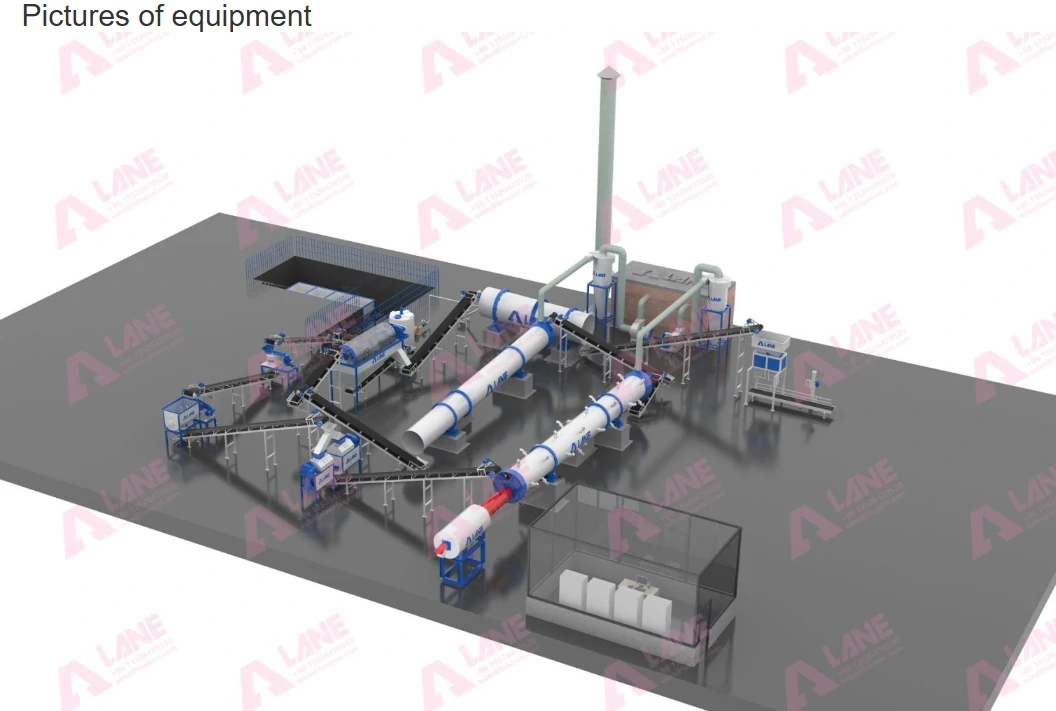
A Calcium Chloride Production Line involves multiple stages, transforming raw materials such as limestone or hydrochloric acid into calcium chloride solutions or solid forms like pellets and flakes. Below is an overview of the key steps involved:
Raw Material Preparation: Limestone or hydrochloric acid is the primary input material. When hydrochloric acid reacts with limestone, it forms calcium chloride as the main product along with carbon dioxide as a byproduct.

Reaction and Mixing: In reactors, the limestone and hydrochloric acid undergo controlled chemical reactions. Depending on the production requirements, the concentration and purity of the solution are monitored to ensure the right formulation.
Evaporation and Concentration: For concentrated calcium chloride solutions, the mixture is passed through evaporators to remove excess water. This stage is crucial for producing industrial-grade calcium chloride solutions used in agriculture, road de-icing, and manufacturing.
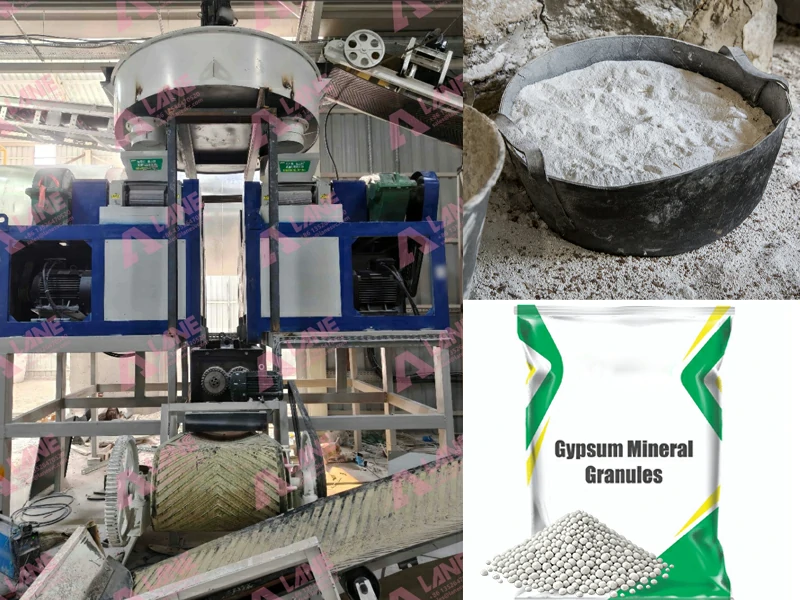
Granulation and Drying: For solid calcium chloride forms such as granules or flakes, the concentrated solution is further processed. Granulators shape the calcium chloride into uniform particles, which are then dried to prevent moisture absorption during storage.

Screening and Packaging: The dried product undergoes screening to ensure uniform size and quality. Once verified, the calcium chloride is packaged in bags or bulk containers, ready for transportation to agricultural suppliers and other industries.
Benefits of Calcium Chloride Production Lines
A reliable Calcium Chloride Production Line offers several benefits, including efficiency, scalability, and quality control. These production lines are designed to operate continuously, meeting the growing demand for calcium chloride across multiple sectors.
In agriculture, the availability of high-quality calcium chloride ensures that farmers have access to effective fertilizers and soil conditioners when needed. With advanced production technologies, manufacturers can produce customized formulations to meet specific agricultural requirements, whether for soil treatments or post-harvest preservation.
The automated processes within modern production lines minimize human error, ensuring consistent quality. This level of precision is essential for industries like agriculture, where the effectiveness of calcium chloride treatments depends on the purity and concentration of the product.
Applications Beyond Agriculture
Calcium chloride’s versatility extends well beyond farming, finding applications in construction, infrastructure, and manufacturing. Its moisture-absorbing properties make it ideal for de-icing roads and highways during winter, preventing ice formation and improving road safety. In industrial settings, calcium chloride is used in concrete accelerators, enabling construction projects to continue even in cold weather.

The chemical is also widely used in the food and beverage industry. For example, it serves as a firming agent for canned vegetables and as an additive in cheese production, where it improves curd formation. Additionally, calcium chloride plays a role in desalination plants, helping remove impurities during water treatment processes.
Sustainability in Calcium Chloride Production
As industries focus on reducing their environmental impact, calcium chloride production lines are adopting more sustainable practices. Modern production facilities employ closed-loop systems that recycle water and reduce chemical waste, minimizing their environmental footprint. Energy-efficient technologies, such as heat recovery systems, are also being integrated into production lines to lower energy consumption.

In agriculture, the use of calcium chloride supports sustainable farming by improving soil health without harmful chemical residues. By enhancing crop quality and reducing post-harvest losses, calcium chloride contributes to food security and reduces food waste, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Challenges in Calcium Chloride Production and Solutions
While calcium chloride production offers many benefits, it also presents some challenges. One issue is the high energy consumption involved in the evaporation and drying processes. To address this, manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient technologies that reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Another challenge is ensuring the consistent quality of raw materials. Variability in the composition of limestone or hydrochloric acid can affect the final product’s purity. Advanced quality control systems are being implemented to monitor raw material inputs and maintain production standards.
Storage and transportation also pose challenges, as calcium chloride is highly hygroscopic and absorbs moisture from the air. Proper packaging and climate-controlled storage facilities are essential to maintain product quality during distribution.
Conclusion
The Calcium Chloride Production Line plays a vital role in agriculture and beyond, providing a reliable supply of calcium chloride for various applications. In agriculture, it supports soil improvement, crop preservation, and efficient nutrient uptake, contributing to higher yields and better crop quality. Beyond farming, calcium chloride’s applications in construction, food production, and infrastructure demonstrate its versatility and value.
As industries embrace sustainable practices, advancements in calcium chloride production will continue to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. By investing in modern production lines, manufacturers can meet the growing demand for calcium chloride while supporting sustainable agriculture and industrial innovation. The future of calcium chloride production holds great potential, helping farmers nourish crops and industries thrive across multiple sectors.





Send a message to us