Ball Mills Operation Guide
Ball mills are essential equipment in various industries, particularly in the production of cement, minerals, and chemicals. Understanding how to operate a ball mill effectively is crucial for maximizing efficiency, ensuring safety, and maintaining product quality. This guide covers the operation, maintenance, and best practices for ball mills.
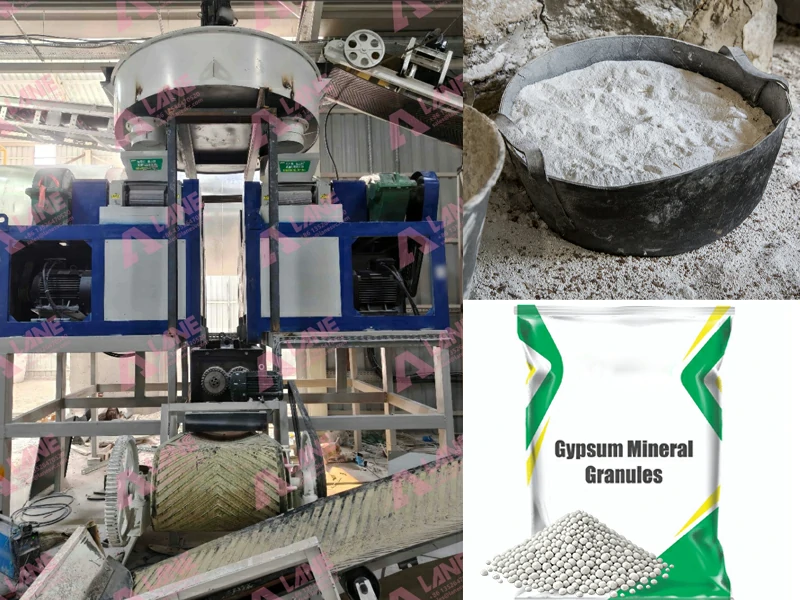
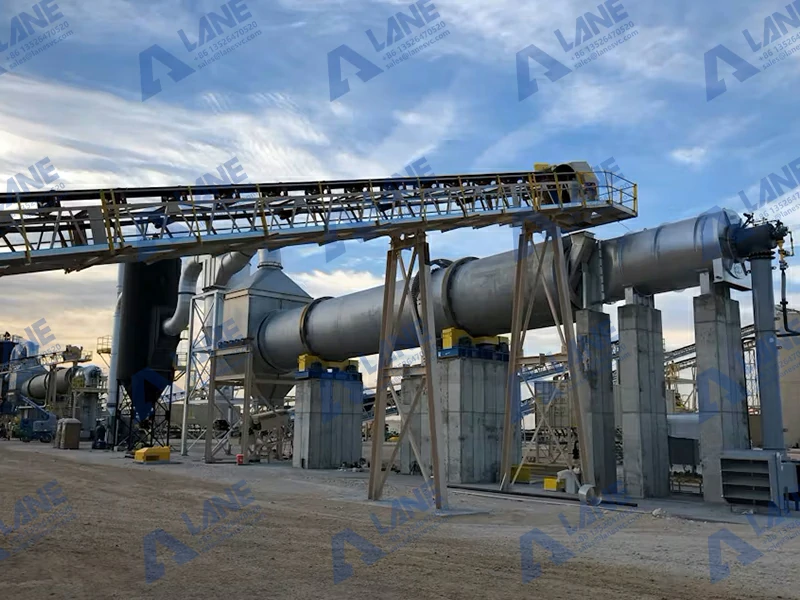
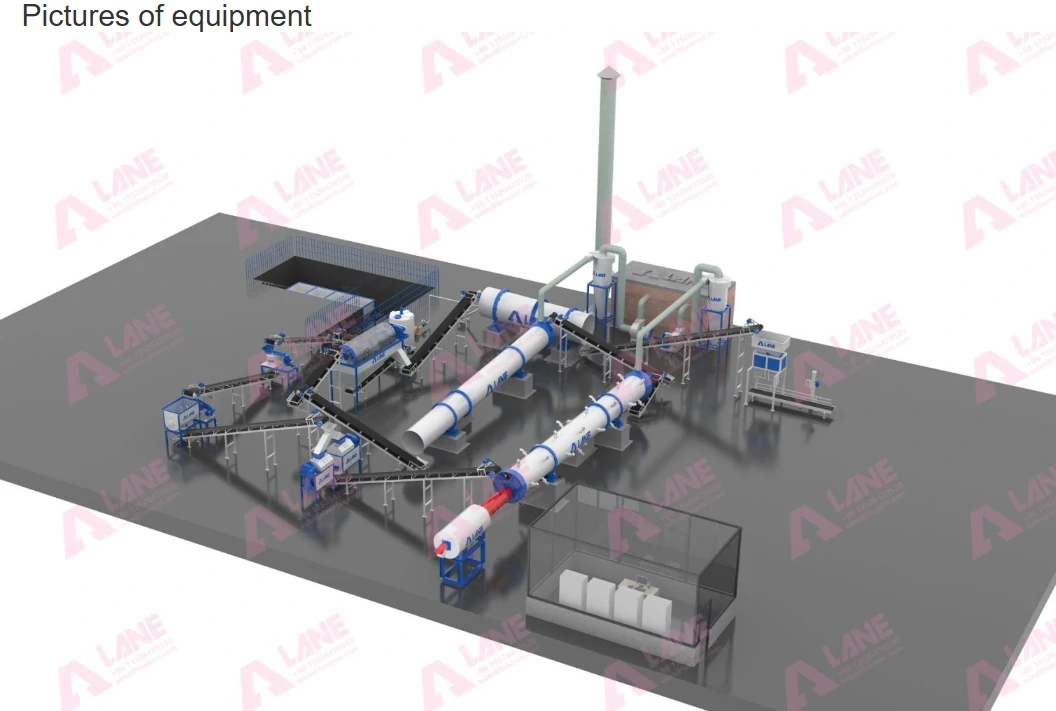
A ball mill is a cylindrical device that rotates around a horizontal axis, partially filled with grinding media (such as balls) and the material to be ground. As the drum rotates, the grinding media exert force on the material, breaking it down into finer particles. This process is essential for producing high-quality end products.
Key Components of Ball Mills

- Drum: The main body where the grinding process occurs. The size and length of the drum can vary depending on the application.
- Grinding Media: Typically steel or ceramic balls that facilitate the grinding process. The size and density of the media influence the grinding efficiency.
- Drive System: Provides the rotational motion to the drum. This can include electric motors, gearboxes, and belts.
- Inlet and Outlet: These openings allow for the introduction of raw materials and the discharge of finished products.
Operating Procedure
Preparation
Before starting ball mills, ensure that all safety precautions are in place. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and hearing protection. Conduct a thorough inspection of the mill to check for any signs of wear or damage.
- Material Selection: Ensure that the materials to be ground are suitable for the ball mill and compatible with the grinding media.

- Feeding the Mill: Load the material into the ball mills through the inlet. It’s essential to adhere to the maximum fill level to prevent overflow and maintain optimal grinding conditions.
Starting the Mill
- Adjust Parameters: Set the operational parameters, including rotational speed and grinding time. The speed should be optimized to prevent excessive wear on the grinding media and drum.
- Engage the Drive System: Start the motor and allow the mill to reach the desired speed gradually. Monitor the operation closely during this phase.
Grinding Process

During the grinding process, it’s essential to maintain a consistent feed rate. This helps ensure that the mill operates efficiently and avoids overloading. The grinding time will vary depending on the material being processed and the desired particle size.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously check for signs of overheating or unusual noise. These could indicate problems with the grinding media, material buildup, or mechanical issues.
- Sampling: Periodically take samples of the material being ground to assess particle size and quality. This allows for adjustments to the grinding time and other parameters if necessary.
Discharge of Material
Once the desired particle size is achieved, it’s time to discharge the material. Stop the mill and allow it to come to a complete stop before opening the outlet. Use appropriate tools to safely remove the ground material.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of ball mills and ensuring consistent performance. This includes:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drum and grinding media to prevent contamination and buildup.
- Inspection: Frequently inspect the grinding media for wear and replace them as needed. Check the drum for any signs of damage or excessive wear.
- Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts, including bearings and gears, are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
Best Practices

- Optimize Loading: Ensure the correct ratio of grinding media to material. A typical ratio is 1:1, but this can vary based on specific requirements.
- Control Temperature: Monitor the temperature during the grinding process. Excessive heat can lead to material degradation or affect the grinding efficiency.
- Use of Additives: Consider using grinding aids or additives to improve efficiency and product quality. These can help reduce energy consumption and enhance flowability.
Safety Consideration
Safety should always be a top priority when operating a ball mill. Ensure that the work area is well-ventilated and free from obstructions. Establish clear safety protocols, including emergency shut-off procedures and proper handling techniques for materials and grinding media.
- Emergency Stops: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop functions of ball mills. Ensure that they are accessible and in working order.
- Material Handling: Use appropriate tools and techniques when loading and unloading materials to minimize the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Operating a ball mill effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of its components, operating procedures, and maintenance practices. By following the guidelines outlined in this operation guide, operators can optimize performance, enhance product quality, and ensure a safe working environment. Regular maintenance and adherence to best practices will not only extend the lifespan of the ball mill but also contribute to efficient and successful production processes. As industries continue to evolve, mastering ball mill operation will remain essential for achieving operational excellence and meeting production goals.





Send a message to us